Table of Contents
Discover the incredible benefits of magnesium foods for your health. Learn how Magnesium Foods boost energy, improve muscle function, and support heart health with delicious magnesium-packed options.
Feeling sluggish or stressed? It might be time to boost your magnesium intake. This essential mineral is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, playing a vital role in muscle and bone health, energy production, and nervous system support. Unfortunately, many people don’t get enough magnesium from their diet, leading to various health issues. In this article, we explore the top magnesium-rich foods that can help you feel a lot better. From dark chocolate to leafy greens, discover delicious options that will enhance your well-being and vitality.
Magnesium deficiency
So this Topic is on magnesium and why you’re gonna feel a lot better if you get enough from your diet .
And if you go to the doctor and you get a blood test and you’re magnesium deficient , it’s not gonna show up because 99% of that magnesium is inside the cell not outside the cell in your blood .
So just because it comes out normal doesn’t mean you’re not deficient .
There’s something called a subclinical deficiency where you might be getting enough to run the basic machinery of the body , but you’re not getting the full amount to run all of the functions .
And as far as magnesium , there are over 300 enzymes involved in many different biochemical reactions that require magnesium .
The importance of magnesium

So out of all the minerals , magnesium is the 2nd most important to potassium .
Why ?
Well , simply because you need a lot of potassium .
Ideally , you you need 300 to 400 milligrams .
Now potassium you need like 47 100 milligrams .
That’s 4,700 milligrams every single day .
So obviously with magnesium you need much less .
But if we compare these minerals to all the other ones you need both of these in pretty large quantities .
90% of all the magnesium is located in the muscle and the bone .
And I did mention this before but 99% of all this magnesium is inside the cell not outside the cell .
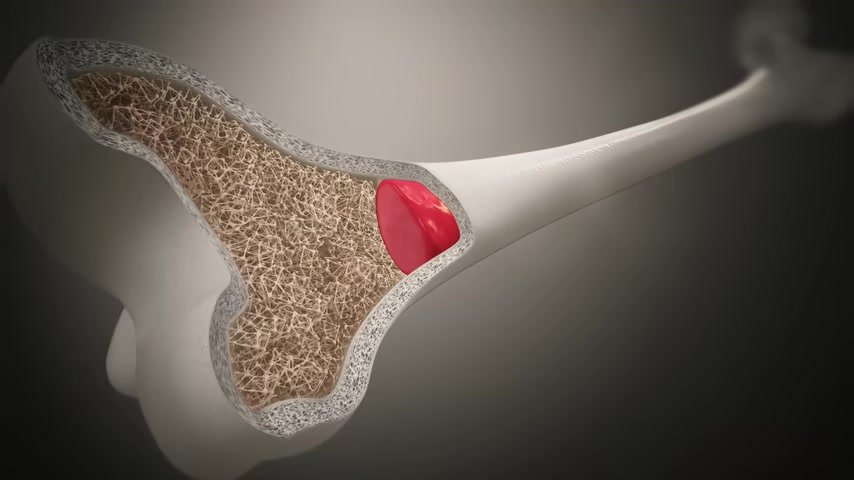
So if you’re deficient , you may have bone problems like osteopenia , eventually osteoporosis .
You can have a lot of muscle cramps , weak muscles .
And also realize that , certain parts of the vascular system have a type of muscle as well .
So if you’re losing magnesium , your muscles can get stiff and you’re gonna get high blood pressure from that .
Another really key function of magnesium is maintaining electrical charge in your cells .
So without magnesium , the electrical system shuts down and you just don’t have enough energy to run the muscles or the nervous system .
So magnesium is really important in keeping , sodium outside the cell , keeping sodium low inside the cell and keeping calcium low inside the cell and keeping potassium high inside the cell .
So we have these different minerals kept apart by this membrane and they all work together to form this battery .
So potassium is involved in this battery also generating energy in the body through what’s called ATP .
It’s involved in making DNA and proteins and overall cell integrity .

So you can imagine if you don’t have enough magnesium , you’re just not gonna feel quite right .
Vascular calcification
Another symptom of a magnesium deficiency , which is subclinical , which means it’s not gonna show up on a test , is vascular calcification .

So calcium and magnesium work together .
So it’s not just about taking too much calcium .
It could be a deficiency in magnesium .
It could also be a deficiency in vitamin k 2 .
The two main causes of a magnesium deficiency
And the two main ways that you’re deficient in magnesium are number 1 , consuming too many refined foods .
Refined carbohydrates like the bread , pasta , cereal , crackers , biscuits , waffles , pancakes , muffins , juice , sugar , as well as just not consuming enough magnesium rich foods , as in leafy greens .
I mean the average person will consume about I think it’s 1.5 cups of vegetables per day .
That’s pathetic .
You need at least 7 , hopefully 10 cups per day .
The average consumption of magnesium

In the hunter gatherer time , Palaeolithic time , they estimated that an average human consumed 600 milligrams of of magnesium per day versus the average person consumes only 200 to 260 milligrams on average .
The RDAs being 300 to 420 , which are not even close to this .
So we are really really deficient in magnesium .
Magnesium Foods

If you don’t feel quite right , you don’t have enough energy , just increase the amount of magnesium in your diet for 1 week and prove it to yourself .
key points:
- If you go to the doctor, and you have a magnesium deficiency, it won’t show up in a blood test. This is because 99% of that magnesium is inside of the cell, not outside of the cell in the blood. Just because the test is normal, doesn’t mean you’re not deficient. There is something called a subclinical deficiency where you might have some magnesium, but not the full amount.
- There are over 300 enzymes that are involved in many different biochemical reactions that require magnesium.
- Out of all of the minerals, magnesium is the second most important to potassium. You need both of these in pretty large quantities. 90% of the magnesium is located in the muscles and bones. If you have low magnesium, you may have bone problems and problems with the muscles like muscle cramps, muscle weakness, or muscle stiffness. Another key function of magnesium is maintaining electrical charge in the cells.
- Another symptom of a subclinical magnesium deficiency is vascular calcification. Calcium and magnesium work together. It’s not just about taking too much calcium. It could be a deficiency in magnesium or a deficiency in vitamin K2.
The two main causes of a magnesium deficiency:
- Consuming too many refined foods
- Not consuming enough foods high in magnesium
If you don’t feel quite right or you don’t have enough energy, consider increasing your magnesium intake for one week and see what happens.
Sources:
Get my FREE PDF Guide on Magnesium 👉 Guide on Magnesium
FAQ:
Why do I feel so much better after taking magnesium?
Taking magnesium can significantly improve your well-being by supporting muscle and nerve function, regulating blood pressure, and promoting restful sleep. It aids in combating depression and anxiety, provides relief from muscle aches, and can enhance exercise performance, contributing to an overall feeling of improved health.
What happens when you increase magnesium intake?
Increasing magnesium intake can lead to various health benefits, including:
- Enhanced bone health
- Reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Lower risk of type 2 diabetes
- Improved mood and fight against depression
- More efficient muscle function and relaxation
What happens if you eat a lot of magnesium?
While magnesium is beneficial, consuming it in excessively high amounts can lead to adverse effects, such as:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Lowered blood pressure
- Muscle weakness
- Irregular heartbeat
Moderation is key, and it’s important to stick within the recommended daily allowances.
Can too much magnesium make you feel?
Too much magnesium can make you feel lethargic, experience stomach upset, or present symptoms of overhydration due to its laxative properties. It’s essential to maintain a balanced intake.
What food is highest in magnesium?
Pumpkin seeds stand out as one of the highest magnesium-rich foods, followed by almonds, spinach, cashews, and black beans. These foods offer a delicious way to meet your daily magnesium needs.
Magnesium-rich foods chart
A magnesium-rich foods chart would categorize foods like nuts, seeds, leafy green vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, detailing their magnesium content per serving. This can serve as a helpful guide to diversifying your diet with magnesium-rich choices.
How much magnesium per day?
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies:
- Men: 400-420 mg/day
- Women: 310-320 mg/day
Children and teens have lower requirements, adjusted as they grow.
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is a highly absorbable form of magnesium, ideal for those looking to supplement their diet. Known for its calming effects on the brain, it is often recommended for those seeking to improve sleep quality or manage anxiety.
Drinks high in magnesium
Mineral water, fortified plant milk, and certain herbal teas can be good sources of dietary magnesium. Additionally, smoothies made with magnesium-rich ingredients like spinach and pumpkin seeds are also excellent.
Magnesium supplement
A magnesium supplement can be a practical choice to ensure you’re meeting your daily needs, especially if your diet may be lacking. It’s available in various forms, including magnesium glycinate, citrate, and chloride.
Foods high in magnesium and potassium
Avocados, spinach, and nuts are not only high in magnesium but also provide a good amount of potassium. These nutrients work together to support muscle and heart function, making them valuable inclusions in your diet.
Magnesium in banana
Bananas are more famous for their potassium content, but they also offer a modest amount of magnesium. One medium-sized banana provides around 32 mg of magnesium.




