Table of Contents
Brief The Article:
What is the importance of zinc?
- Zinc is involved in 300 different enzymes and over 1000 factors related to DNA
- It plays a crucial role in digestion, wound healing, and immune function
- Zinc deficiency can lead to serious health issues if not addressed early
Side effects of zinc deficiency
- Loss of appetite and anorexia
- Impaired wound healing and development of ulcers
- Hypogonadism (testicular atrophy) and low testosterone
- Thymus gland atrophy, leading to compromised immune system
- Increased cortisol levels
- Muscle loss
What is the most common sign of zinc deficiency?
- Foul-smelling stool that floats
- Other symptoms may include cramping, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating
- Shortness of breath upon exertion is another early indicator
What causes zinc deficiency?
- Insufficient dietary zinc intake
- Gut malabsorption and inflammation
- Consumption of foods high in phytates (e.g., grains, refined carbs)
- Low consumption of meats, especially red meat
- High sugar intake, diabetes, excessive stress, regular alcohol consumption, and infections
The best sources of zinc
- Oysters
- Crab
- Other shellfish
- Meats
- Fish
- Cashews and peanuts (in smaller amounts)
What does zinc do in the body?
- Regulates sleep cycles
- Supports hippocampus function (memory, learning, cognitive function)
- Involved in insulin regulation
- Aids in neurotransmitter production (serotonin, dopamine)
- Forms important antioxidants for brain, heart, and muscles
- Helps manage oxidative stress in mitochondria
Today I’m going to share some very important information about zinc, and the reason I’m talking about zinc is that zinc is involved in so many different things. It’s involved in 300 different enzymes and over a thousand different factors related to your DNA. Its functions are very wide, helping certain enzymes not just for digestion, but for a lot of other things. But did you know about the incredible benefits of zinc?
This essential mineral plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health, and understanding the benefits of zinc can empower you to take control of your well-being. From supporting a robust immune system to promoting healthy cell growth, the benefits of zinc are truly remarkable.
In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of zinc and explore the numerous benefits of zinc for your body. Get ready to unlock the power of this essential mineral and discover how it can contribute to a healthier, more vibrant you!
So let’s dive into the details…
Zinc: The Importance and Impact of this Essential Mineral

Today I’m going to share some very important information about zinc, and the reason I’m talking about zinc is that zinc is involved in so many different things. It’s involved in 300 different enzymes and over a thousand different factors related to your DNA. Its functions are very wide, helping certain enzymes not just for digestion, but for a lot of other things.
- Zinc is involved in 300 different enzymes.
- Zinc is involved in over 1000 different factors related to your DNA.
- Zinc helps enzymes involved in digestion and other bodily functions.
Zinc Explained: Understanding Zinc Deficiency
And if you can identify early signs of a zinc deficiency, sometimes they call it a subclinical deficiency, then you can prevent advanced problems related to zinc. And that could include a complete loss of appetite, and then you end up having anorexia necrosis because the tissue is not healing.
- Early signs of zinc deficiency are often subclinical.
- Advanced zinc deficiency can lead to loss of appetite and anorexia necrosis.
- Zinc is crucial for tissue healing.
Side Effects of Zinc Deficiency: Beyond Tissue Healing
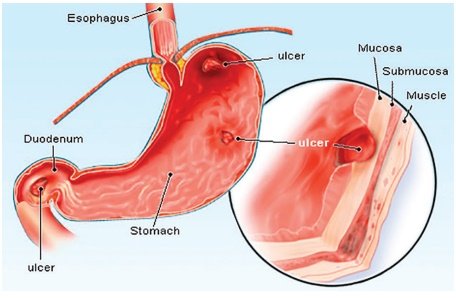
And so zinc actually helps with wound healing, and if you’re deficient in zinc, you can develop ulcers externally or internally on your body, even ulcers in your mouth. And even some elderly that have these ulcers because they’re in this bed and they’re unhealing ulcers or wounds they need zinc big time.
- Zinc deficiency can cause ulcers internally and externally.
- Zinc aids in wound healing, especially important for the elderly.
Hypogonadism and Thymus Atrophy: More Serious Consequences
Another Advanced problem with zinc is hypogonadism where your testicles actually atrophy or shrink. So you’re obviously going to have low testosterone, that could be an advanced zinc deficiency. And I’m going to put all this research Down Below in the description. Another interesting advanced problem would be thymus atrophy.
- Hypogonadism (testicular atrophy) and low testosterone can result from zinc deficiency.
- Research linked in the description.
- Zinc deficiency can lead to thymus atrophy, impacting the immune system.
The Impact on Cortisol, Muscle Loss, and Oxidative Damage
The thymus gland is on top of the heart, and that has a huge influence on making certain T cells that are involved with the immune system.
It’s like a training camp for your immune system, and if you have atrophy of the thymus gland, could you imagine what’s going to happen to your immune system? You’re not going to have an immune system!
Then we have the adrenal hormone called cortisol. Your cortisol can greatly go up if you’re deficient in zinc, which could be the reason why it affects the thymus, the immune system, because when you have high cortisol that can paralyze the immune system in the white blood cell.
- Thymus atrophy weakens the immune system.
- Zinc deficiency can elevate cortisol levels, further suppressing the immune system.
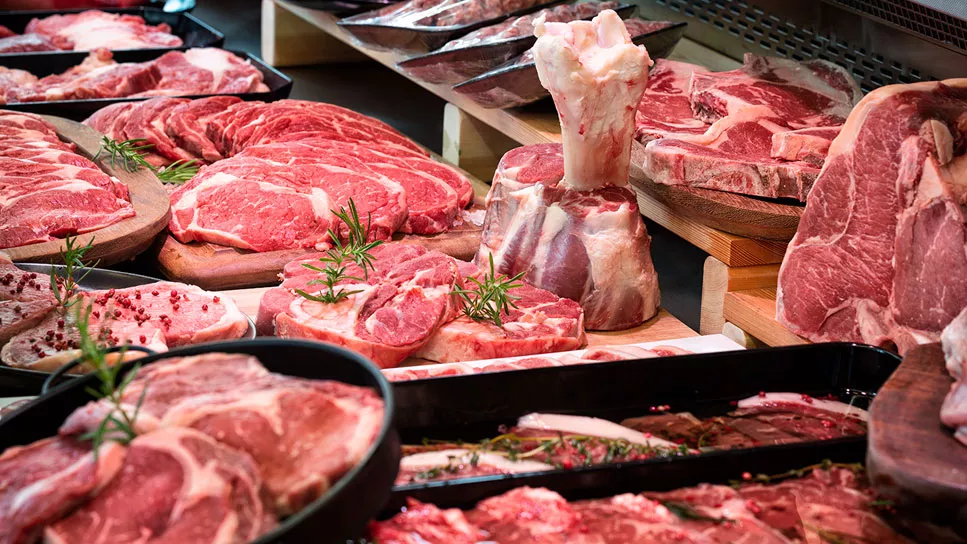

You also have muscle loss because of the involvement with zinc. In fact, one of the best sources of zinc is in animal meat because we need that zinc in our muscles to create antioxidants to counter all the oxidative damage that occurs, especially with exercise.
- Zinc deficiency contributes to muscle loss.
- Animal meat is a rich source of zinc, important for muscle antioxidant production.
The Most Common Sign of Zinc Deficiency: Digestive Distress

So if you could identify early signs of a zinc deficiency, you can head off or prevent bigger problems and I wanted to show you one of my favorite books. It’s called the technology of War by Sun Tzu, you probably heard of The Art of War right, but this book is a lot different.
If you take a look at some of the um the books on Art of War, there’s like 45 different versions, a lot of them are altered from the original translation. T
his book is an exact duplication of the original text that Sun Tzu wrote in Chinese. In this section, he’s talking about Supreme skill is not 100 Victories in 100 Battles. Supreme skill is subduing the enemy’s operations and its forces without battle.
And if we can relate this to this topic on your body, which I do all the time, you don’t want to wait until you have an advanced disease before you do something about it.
If you understand the early signs or the symptoms of something, you can easily prevent it because you have the knowledge.
So that way, understanding your body’s early signs for something is extremely valuable and I have a lot of topics on that. So let’s talk about the most common early sign of a zinc deficiency.
Well, first of all, you have to have the intelligence or understanding of where zinc tends to affect certain organs more than others and it just so happens that the organ that is most affected by a zinc deficiency is the pancreas okay.
- Understanding early signs of deficiency is key for prevention.
- The pancreas is highly susceptible to zinc deficiency.
Understanding the Pancreas and Zinc’s Role
Now there’s two parts of the pancreas. You have one that controls your blood sugars which has to do with insulin which zinc has a lot to do with, but also the other part is called the exocrine part of the gland which has to do with enzymes okay.
- The pancreas has two parts: endocrine (blood sugar/insulin) and exocrine (enzymes).
- Zinc plays a significant role in both pancreatic functions.
Foul-Smelling Stool: A Key Indicator
And so this is the symptom, are you ready for this? Foul-smelling stool that floats. Yeah, that’s right. You might have some cramping, you might have a little diarrhea, you might have abdominal pain, you might even have bloating okay.
- Foul-smelling, floating stool is a common early sign of zinc deficiency.
- May be accompanied by cramping, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating.
But this is a very easy thing to identify and yes it could come from other things too. It could come from what you just ate, but it can also come from a zinc deficiency.
And just as a side note I did another topic about this I think four years ago and there is another common first symptom which is shortness of breath upon exertion which is another indicator which is good to know because sometimes people think well I’m just out of shape. Well, it could be a zinc deficiency.
Zinc Deficiency Causes: Diet, Malabsorption, and More

So we need to look at the diet. Are you eating enough zinc or maybe it’s coming from what’s called gut malabsorption? Maybe you have inflammation your gut uh that’s a big cause of a zinc deficiency. Another cause of a zinc deficiency is consuming something with something called phytates okay or phytic acid which is in grains.
- Shortness of breath upon exertion can also be an early sign of zinc deficiency.
- Dietary factors, gut malabsorption, and inflammation can contribute to zinc deficiency.
- Phytates (phytic acid) in grains can inhibit zinc absorption.
If you are a cereal eater if you eat a lot of refined carbs, you’re going to get phytic acid and that is going to potentially create a zinc deficiency.
There’s millions of children that have a zinc deficiency around the world that are consuming a lot of cereal. They don’t consume a lot of meats, especially red meat and then they end up with this diarrhea which is very very dangerous.
The Best Sources of Zinc: Oysters, Meat, and More
And out of all the foods that are the highest in zinc, it’s oysters okay. And then you have crab, other shellfish, meats, fish and then you might have some zinc in cashews and peanuts but you want to just look at the whole situation to see could this situation be coming from my diet?
- High cereal consumption and low meat intake can contribute to zinc deficiency, especially in children.
- Oysters are the richest source of zinc, followed by crab, shellfish, meats, and fish.
- Cashews and peanuts also contain zinc.
Other Factors Contributing to Zinc Deficiency

Is it coming from something that I’m eating that’s creating this deficiency? Because also sugar or even being a diabetic and credit deficiency, too much stress can create a deficiency in zinc.
Or let’s say for example you drink alcohol on a regular basis that could create a zinc deficiency okay. Having an infection can create the deficiency of zinc.
- Sugar,
- diabetes,
- stress,
- alcohol consumption,
- infections can also contribute to zinc deficiency.
So I think it’s very important to use principles like this to be able to predict and to be able to predict you have to have the right information.
You have to have all of the information to be able to understand the consequences or the early signs of something that can lead into something bigger because typically what would you do if you have a symptom like a digestive issue?
You might go to the doctor, it gives you a pill, it masks the symptom, your symptom is better, the problem is still there and then it kind of goes downhill from there.
What Does Zinc Do? A Multifaceted Mineral

And just to give you a little more Intel or information on zinc, zinc is very much involved with your sleep cycles.
- Understanding the early signs of zinc deficiency is crucial for preventing more serious health issues.
- Zinc plays a vital role in sleep regulation.
If you have sleep problems let’s say you don’t get enough of the last part of your sleep, zinc could be something you might want to take right before bed.
Zinc is also heavily involved in a part of your brain called the hippocampus which is kind of like the relay part for memory and learning and cognitive function.
- Zinc can be beneficial for sleep problems, especially difficulties with the later stages of sleep.
- Zinc is crucial for hippocampal function, supporting memory, learning, and cognitive function.
Zinc is also like I said before involved with insulin okay. If you don’t have enough zinc it can put you at risk for becoming a diabetic.
Zinc is also involved in making neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine which can affect your mood.
- Zinc deficiency can increase the risk of developing diabetes.
- Zinc is involved in the production of serotonin and dopamine, impacting mood regulation.
And zinc also makes up a very important group of antioxidants involved with your brain your heart and your muscles the three parts of your body that use a lot of oxygen.
And if we look a little bit deeper zinc helps with this oxidative stress that’s involved with your mitochondria the energy factory of all these tissues.
- Zinc is a component of important antioxidants, protecting the brain, heart, and muscles from oxidative stress.
- Zinc supports mitochondrial function, the energy powerhouse of cells.
Recognizing the Importance of Prevention
So I want you to start looking at these symptoms a little bit differently instead of just jumping and treating them try to understand what your body is telling you.
Realize that a lot of these problems could be related to a nutritional deficiency that could be related to your diet and use these indicators or little red flags as something that you can have advanced knowledge or prediction to then prevent something.
But unfortunately, this idea of prevention you can’t really talk too much about it because even like on the bottles of different nutrients you’ll see there’s a mandatory label says this product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease so it’s illegal to even prevent a disease.
So what I try to do in my topics is to give you the knowledge of what you could end up with so then that way you don’t have to end up with a situation you’re battling it which is a lot more work.
- Understanding the body’s signals can help identify potential nutritional deficiencies and prevent future health problems.
Learn More about the Dark Side of Zinc!
It is so much easier to win the war by doing something like this than going into battle with a health condition. Now if you haven’t seen my recent topic on the the Dark Side of zinc, I put it up right here check it out.
- Prevention is key to maintaining optimal health.
Summary
- Zinc is involved in your sleep cycles, cognitive function, and making neurotransmitters. Having low zinc increases your risk of diabetes.
- Zinc also makes up an important group of antioxidants involved with your brain, heart, and muscles. It even helps reduce oxidative stress involved with the mitochondria.
- Instead of masking a symptom related to zinc deficiency or any other health issue, it’s crucial to get to the deeper problem to help prevent further concerns. Learning how to support a healthy body and avoid health issues or recognize the early stages of one is much more simple than trying to fight a health problem.
Side effects of advanced zinc deficiency can include:
• Loss of appetite
• Necrosis
• Ulcers
• Hypogonadism
• Low testosterone
• Thymus atrophy
• High cortisol
• Muscle loss
The organ that is most affected by zinc deficiency is the pancreas. The most common early sign of zinc deficiency is foul-smelling stool that floats.
Other early signs of zinc deficiency include:
- Shortness of breath upon exertion
• Cramping
• Diarrhea
• Abdominal pain
• Bloating
Top causes of zinc deficiency:
• Lack of zinc in the diet
• Malabsorption
• Inflammation in the gut
• Phytates or phytic acid (grains)
• Consuming sugar
• Diabetes
• Stress
• Drinking alcohol
• Infection
Foods rich in zinc:
- Oysters
- Crab
- Other shellfish
- Meats
- Fish
- Nuts
Additional Resources:
- NCBI: Zinc in Human Health
- Cambridge: Subclinical Zinc Deficiency Study
- Global Health Research: Zinc Deficiency
- Tropical Gastroenterology: Zinc-Copper Ratio
FAQ
What is unique about zinc?
Zinc is unique among essential minerals due to its versatile role in human health:
- It’s involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body
- Zinc is crucial for immune function, DNA synthesis, and cell division
- It’s the second most abundant trace mineral in the human body after iron
- Zinc has antioxidant properties, protecting cells from oxidative stress
- It plays a vital role in growth, development, and wound healing
What is the unique nature of zinc?
The unique nature of zinc stems from its chemical and biological properties:
- It’s the only metal that appears in all enzyme classes
- Zinc can act as both a catalyst and a structural component in proteins
- It has the ability to form stable complexes with various organic ligands
- Zinc doesn’t undergo redox reactions, making it a stable cofactor
- Its small size and high charge density allow for versatile biological functions
What are the Benefits of zinc?
Zinc offers numerous health benefits:
- Boosts immune system function
- Promotes wound healing
- Supports protein and DNA synthesis
- Aids in growth and development
- Enhances taste and smell perception
- Supports eye health and may reduce age-related vision decline
- May help reduce the duration and severity of common colds
- Supports skin health and may help with acne
What is the Speciality of zinc?
The specialty of zinc lies in its multifaceted roles in the body:
- It’s essential for the activity of over 2000 transcription factors
- Zinc is crucial for male reproductive health and testosterone production
- It plays a key role in insulin storage and release
- Zinc is involved in neurotransmitter function and brain health
- It’s important for maintaining the integrity of skin and mucous membranes
- Zinc has anti-inflammatory properties
Benefits of zinc sexually
Zinc plays a significant role in sexual health, particularly for men:
- Supports healthy testosterone levels
- Aids in sperm production and motility
- May help improve erectile function
- Supports prostate health
- Can boost libido in cases of zinc deficiency
- May enhance fertility in both men and women
Zinc benefits for women
Zinc offers several benefits specific to women’s health:
- Supports reproductive health and fertility
- May help regulate menstrual cycles
- Important for fetal development during pregnancy
- Can help reduce severity of PMS symptoms
- Supports breast health
- May help balance hormones
- Supports healthy skin, hair, and nails
Zinc Tablets benefits
Zinc tablets can provide various benefits, especially for those with deficiency:
- Convenient way to meet daily zinc requirements
- Can boost immune function
- May help with wound healing
- Can support cognitive function
- May help improve acne and skin health
- Can aid in protein synthesis and muscle repair
- Useful for addressing zinc deficiency symptoms
Is 50mg of zinc too much?
50mg of zinc is generally considered above the recommended daily intake:
- The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for adults is 8-11mg
- The upper limit is set at 40mg per day for adults
- Consuming 50mg regularly may lead to adverse effects over time
- Short-term use of 50mg may be prescribed for specific conditions
- Excess zinc can interfere with copper absorption
- Always consult a healthcare provider before taking high doses
Benefits of zinc for men
Zinc offers several specific benefits for men’s health:
- Supports healthy testosterone levels
- Crucial for prostate health
- Aids in sperm production and quality
- May help prevent and treat erectile dysfunction
- Supports muscle growth and repair
- Can help maintain cognitive function
- Important for male pattern baldness prevention
How much zinc per day for a woman?
The recommended daily zinc intake for women varies:
- Adult women (19+ years): 8mg per day
- Pregnant women: 11mg per day
- Breastfeeding women: 12mg per day
- Women on oral contraceptives may need slightly more
- Upper limit for adult women is 40mg per day
- Individual needs may vary based on diet and health conditions
Zinc benefits for skin
Zinc offers several benefits for skin health:
- Has anti-inflammatory properties, helpful for acne and rosacea
- Acts as a natural sunscreen, protecting against UV damage
- Aids in collagen synthesis, promoting skin elasticity
- Helps regulate oil production in the skin
- Supports wound healing and scar reduction
- May help with eczema and psoriasis symptoms
- Acts as an antioxidant, protecting skin from free radical damage
Daily dose of zinc for adults
The recommended daily dose of zinc for adults varies:
- Adult men (19+ years): 11mg per day
- Adult women (19+ years): 8mg per day
- Pregnant women: 11mg per day
- Breastfeeding women: 12mg per day
- Upper limit for all adults: 40mg per day
- Vegetarians may need up to 50% more due to lower bioavailability
- Individual needs may vary based on diet, health conditions, and lifestyle




