Table of Contents
Ditch the outdated myths! See Why Should Eat 2-4 Eggs Daily, Eggs are nutritional powerhouses, packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and easily digestible protein. Discover how Eating 2-4 Eggs Daily can transform your health, boosting everything from your skin and hair to your brainpower and energy levels.
Are Eggs Healthy?

There are quite a few reasons why you should be consuming two to four eggs every single day. Now the egg is really considered a perfect food, not just a perfect protein.
It’s low carb, it’s higher fat, and it’s high-quality moderate protein. Out of all the proteins– I’m talking about beef, chicken, fish, lamb, pork – all these other proteins are muscle protein.
An egg is a completely different type of protein, it’s the most bioavailable of all proteins – the most efficient protein. When you’re digesting it, you get the least amount of waste, which then turns into glucose.
So out of all the different proteins you can eat, definitely, eggs rank number one. Not to mention eggs have a complete profile of essential amino acids.digestingThere are quite a few reasons why you should be consuming two to four eggs every single day.
Now the egg is really considered a perfect food, not just a perfect protein. It’s low carb, it’s higher fat, and it’s high-quality moderate protein. Out of all the proteins– I’m talking about beef, chicken, fish, lamb, pork – all these other proteins are muscle protein.
An egg is a completely different type of protein, it’s the most bioavailable of all proteins – the most efficient protein.

When you’re digesting it, you get the least amount of waste, which then turns into glucose. So out of all the different proteins you can eat, definitely, eggs rank number one. Not to mention eggs have a complete profile of essential amino acids.
- Eggs are a “perfect food”: Low carb, higher in healthy fats, and a source of high-quality protein.
- Most bioavailable protein source: Offers efficient digestion and minimal waste.
- Complete amino acid profile: Provides all essential amino acids needed by the body.
Egg Whites vs. Egg Yolks

So today I’m going to talk about the benefits of eggs but primarily for your skin and your hair. I’m also going to cover some data on whether you should eat raw eggs or cooked eggs.
I’ll talk about allergies and a couple of other points. So let’s start from the top. Now the protein in eggs, believe it or not, is not just in the egg white – it’s also in an egg yolk.
In fact, there’s more protein in the yolk, okay, than there is white if you actually do a comparison of equal value as far as weight goes.
So if you’re just eating egg whites you’re missing out not only on additional protein but a lot of other nutrients. But the egg yolk is super concentrated in fat-soluble vitamins, which really support the skin and especially your hair.
- Both egg whites and yolks contain protein: However, yolks actually contain more protein than whites.
- Egg yolks are nutrient-dense: Rich in fat-soluble vitamins that are beneficial for skin and hair health.
Egg Benefits
It’s really difficult to find foods that have the active form of vitamin A – retinol – but egg yolk is at the top of the list. And vitamin A is really important in skin health.
If you’re deficient, your skin is going to be rough and dry. Vitamin A is also very important for your eyes as well as your sinuses and the immune system and many other additional things.
Now one point about vitamin A that’s interesting is in the definitions of vitamin A, they include beta-carotene, which is a precursor to vitamin A, to be vitamin A. When, in fact, it’s really a precursor – it’s not retinol.
So when you do your analysis on nutritional density in foods, a lot of times you’ll see, like in kale or spinach, there’s all this vitamin A, but it’s actually the precursor beta carotene. So when we’re talking about all the benefits of vitamin A, we’re talking about the bioavailable form: retinol, not beta-carotene.
- Excellent source of retinol: Provides the active form of Vitamin A, essential for healthy skin, eyes, immune function, and more.
- Important distinction between retinol and beta-carotene: While many foods contain beta-carotene (a precursor to vitamin A), eggs offer the directly usable retinol form.
Vitamin D, E, K, Choline, and Omega-3s
Now vitamin D is also in eggs, and out of all the vitamins, vitamin D is right at the top of the list as far as the importance for the skin.

If you’re deficient in vitamin D you can have everything from rashes to sun sensitivity to sunspots to psoriasis – all sorts of problems occur in the skin if you’re deficient in vitamin D.
And also you’ll have more inflammation and more acne. And as far as vitamin D and foods, in general, it’s not very easy to find vitamin D foods. But eggs are one of the foods that actually contains vitamin D.
All right, vitamin E is that important for your skin? You better believe it! It protects the skin against UV radiation, it helps break down scarring, it acts as a powerful antioxidant for the skin, as well as internally as well.
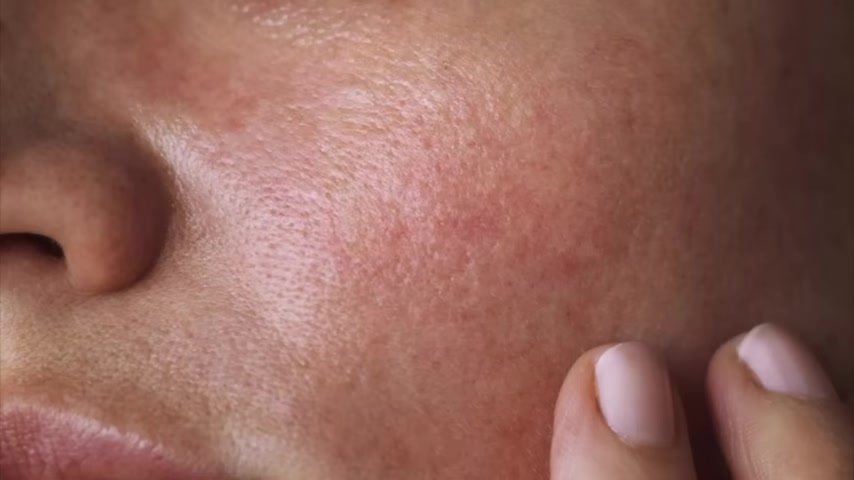
Then we have vitamin K1 and vitamin K2. Eggs are loaded with choline, which is a nutrient that prevents a fatty liver from occurring.
It also is essential for brain and nerve health, which includes keeping your mood high and also improving your memory. Eggs also contain a good amount of omega-3 fatty acids – another great thing for your skin as well as a good anti-inflammatory.
- Vitamin D for skin health: Aids in preventing skin issues such as rashes, sun sensitivity, and psoriasis.
- Vitamin E for protection and repair: Protects against UV damage, helps with scar reduction, and acts as an antioxidant.
- Vitamins K1 and K2, choline, and Omega-3s: Offer a range of benefits for liver health, brain function, mood, memory, skin health, and reducing inflammation.
Cholesterol and Lecithin
Eggs also are loaded with lesser-known lecithin, the antidote to cholesterol. So if you’re concerned about cholesterol eating eggs, you don’t have to be concerned – eggs will increase your HDL, and if there’s any extra cholesterol in your body lecithin will help counter that excess cholesterol.
Choline, as well… Eggs are loaded with B vitamins, okay, especially B2, B3, B12, and biotin, which is good for the hair.
- Lecithin counteracts cholesterol: Helps mitigate cholesterol intake and promotes healthy HDL levels.
- Rich in B Vitamins: Abundant in B2, B3, B12, and biotin, all beneficial for hair health and other bodily functions.
Raw Eggs vs. Cooked Eggs
Now, since we’re on the topic of biotin I should go right to this right here – raw eggs. What’s my thought about eating raw eggs?
Now here’s the thing: in the egg yolk, there is this compound called avidin, and avidin binds with biotin, making it unavailable for you to absorb, okay?
So, if you consume a lot of eggs over a long period of time, you’ll probably become deficient in biotin and that can affect your hair. But you would have to consume a lot of raw eggs over a long period of time.
The other point I want to make about raw eggs is there are enzyme inhibitors, okay? So, potentially, it could inhibit the digestion of proteins. I think a little bit of raw eggs would be fine but I wouldn’t do a large amount over a long period of time.
- Avidin in raw egg yolks can block biotin absorption: While eggs are a good source of biotin, consuming them raw in large quantities over time can hinder biotin absorption.
- Raw eggs contain enzyme inhibitors: These can potentially interfere with protein digestion, making cooked eggs a better choice.
Salmonella Concerns

Now, what about the point of getting salmonella in raw eggs? Well, the odds of you getting salmonella are one in thirty thousand. You’d have to consume five eggs a day for about 15 years before there’s a chance of getting salmonella.
Salmonella comes from sick chickens – chickens that have an altered microbiome. But if you’re consuming the eggs that I recommend, which are not commercial eggs – okay, I’m recommending pasture-raised organic eggs – the chance of you getting salmonella are much much less than winning the Virginia lottery, okay?
- Salmonella risk is low: The chances of contracting salmonella from eggs are very slim, especially if consuming pasture-raised organic eggs.
Pasteurized vs. Pastured Eggs

So now I also run into this – this word pasteurized, okay? You have pasteurized and pastured – okay, two different words here.
They do sometimes have pasteurized eggs at the grocery store, okay? Now, what does that mean? Well, since there might be a chance of getting some microbial infection on the surface of the egg – okay the shell, like salmonella – they pasteurize the egg.
They heat it up to a certain degree, not to cook the inside of the egg, but just to heat up the outside to sterilize the eggs. So when you see pasteurized eggs that’s really what’s occurring.
Now, when you have pastured eggs we’re talking about chickens that roam around on different pastures, being able to eat bugs and worms and grass – this is the type of egg that you want.
- Pasteurization vs. Pastured:
- Pasteurization heats eggs to eliminate potential surface bacteria but does not affect the inside.
- Pastured eggs come from chickens raised in more natural settings with access to a diverse diet.
Egg Allergies and Oxidized Cholesterol
Now, when someone has an allergy to eggs, it’s to the egg white, okay? Not the yolk. So if you do have an egg allergy, what you could do is just eat the yolks, okay?
That way you can get some protein, you also can get the benefit of all these things I’m talking about right here.
Another point that people bring up when they talk about raw eggs is that they don’t want to cook the egg because they don’t want oxidized cholesterol.

Well, you’re not going to get oxidized cholesterol if you even scramble an egg. You would get oxidized cholesterol if you were to take this egg and put it through a high-pressure device through small little particles, okay? That’s how you’re going to get oxidized cholesterol.
- Egg allergies usually pertain to egg whites: Individuals with egg allergies may still be able to consume yolks.
- Cooking eggs does not oxidize cholesterol: Oxidized cholesterol formation is unlikely from regular cooking methods.
Minerals and Carotenoids
There is a good amount of minerals in eggs – there’s potassium, there’s magnesium, there’s also iodine, another very important trace mineral that is not in a lot of foods but it’s in eggs.
And selenium, which is very important for your thyroid in converting T4 to T3. The other cool thing that’s in eggs is these carotenoids. Carotenoids include hundreds of different compounds. These are two powerhouses – lutein and zeaxanthin, okay?
So, both of these carotenoids greatly support the skin because they’re antioxidants, as well as the eye, protecting you against macular degeneration, cataracts, and skin damage from the sun. And the bioavailability of these carotenoids in eggs are much better than in vegetables.
- Eggs are rich in essential minerals: Contain potassium, magnesium, iodine, and selenium.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin for eye and skin health: Eggs provide these potent antioxidants that protect against macular degeneration, cataracts, and sun damage.
Summary
Eggs contain protein in both the whites and yolks. There is actually more protein in the egg yolk than in the white. If you only consume egg whites, you’re missing out on extra protein and a lot of nutrients.
The top benefits of eggs:
- Egg yolks are super concentrated in fat-soluble vitamins, including:
• Vitamin A – supports the skin, eyes, and immune system
• Vitamin D – supports the skin and reduces inflammation
• Vitamin E – protects against UV radiation and helps break down scarring
• Vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 - Eggs are loaded with choline, which helps support your:
• Liver
• Brain
• Nerves
• Mood
• Memory - Eggs are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support the skin and have anti-inflammatory properties
- Eggs are loaded with lecithin, which helps counter excess cholesterol
- Eggs have B vitamins, which are great for your hair and many other areas of your health
- Eggs contain minerals, iodine, and selenium to support a healthy body
- Eggs are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, which are carotenoids that support the skin and eyes
DATA
https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/food-features/eggs/
FAQ
Why you should eat 2 to 4 eggs a day?
Eating 2 to 4 eggs daily can provide numerous health benefits. Eggs are nutrient-dense, containing high-quality protein, essential vitamins, and minerals. They are particularly rich in:
- Vitamin B12: Important for nerve function and the production of DNA and red blood cells.
- Choline: Crucial for brain health and development.
- Selenium: An antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
Additionally, eggs are known to promote satiety, which can aid in weight management by reducing overall calorie intake throughout the day. Regular consumption of eggs has also been linked to improved heart health and better eye health due to their nutrient profile[2][5].
What happens if I eat 2 eggs every day?
Consuming 2 eggs daily is generally considered safe for most individuals and can lead to several positive health outcomes. Regular egg consumption can help improve muscle strength, support weight management, and provide essential nutrients that may be lacking in other parts of the diet. However, for individuals with specific health conditions, such as diabetes or high cholesterol, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor dietary choices accordingly[2][3].
Is 3 eggs a day too much?
Research indicates that eating up to 3 whole eggs per day is safe for most healthy individuals. Studies have shown that this level of consumption does not significantly impact cholesterol levels for the majority of people. In fact, eggs can be beneficial for heart health, as they contain omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients that support cardiovascular function. However, individual responses may vary, and those with specific health concerns should seek medical advice[2][4].
Is it safe to eat 5 eggs a day?
While there is limited research on the long-term effects of consuming 5 eggs daily, most studies suggest that moderate consumption (up to 3 eggs) is safe for healthy individuals. Eating 5 eggs may not be harmful for some; however, it could lead to excessive cholesterol intake for others, particularly those sensitive to dietary cholesterol. It’s essential to monitor overall dietary patterns and consult with a healthcare professional if considering higher egg consumption[3][4].
Side effects of eating eggs every day
Eating eggs daily can lead to some side effects for certain individuals, particularly those with specific health issues. Potential side effects include:
- Increased cholesterol levels: For a small percentage of the population, dietary cholesterol can significantly impact blood cholesterol levels.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may have an allergy to egg proteins, leading to various allergic symptoms.
- Digestive issues: Overconsumption of eggs may lead to digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals.
However, for most people, the benefits of consuming eggs outweigh the potential risks, especially when balanced with a healthy diet[2][3].
4 eggs a day benefits
Consuming 4 eggs a day can provide enhanced benefits, including:
- High protein intake: Supports muscle repair and growth.
- Increased nutrient density: Provides significant amounts of vitamins A, D, E, B12, and choline.
- Weight management: High protein content can help with satiety, potentially reducing overall calorie intake.
- Heart health support: Nutrients in eggs can help improve cholesterol profiles and reduce the risk of heart disease[2][5].
Will I gain weight if I eat 2 eggs a day?
Eating 2 eggs a day alone is unlikely to cause weight gain, especially if they are part of a balanced diet. Eggs are satiating, which can help control hunger and reduce overall calorie intake. However, weight gain occurs when there is a consistent caloric surplus, so it’s essential to consider overall dietary habits and lifestyle factors[2][4].
How many boiled eggs should I eat a day?
The recommended number of boiled eggs varies based on individual health goals and dietary needs. Generally, consuming 1 to 3 boiled eggs per day is considered safe and beneficial for most people. It’s important to balance egg intake with other protein sources and nutrients to ensure a well-rounded diet[3][5].
What happens if I eat eggs for breakfast every day?
Eating eggs for breakfast every day can lead to several positive outcomes, including:
- Improved satiety: Eggs are high in protein, which can keep you feeling full longer.
- Better nutrient intake: Starting your day with eggs can help you meet your daily nutritional needs.
- Enhanced weight management: Regularly consuming protein-rich breakfasts has been linked to lower calorie intake throughout the day[2][4].
Benefits of eating 2 eggs daily
Eating 2 eggs daily can provide numerous health benefits, such as:
- High-quality protein source: Essential for muscle health and repair.
- Rich in vitamins and minerals: Supports overall health and well-being.
- Potential weight loss aid: Helps control hunger and reduce calorie intake.
- Supports brain health: Choline in eggs is vital for cognitive function[2][5].
What happens if you eat 2 eggs a day?
Consuming 2 eggs a day can lead to improved nutritional status, enhanced satiety, and better overall health outcomes. Most individuals will not experience adverse effects, and the high protein and nutrient content can support various bodily functions[2][3].
Will you gain weight if you eat eggs every day?
Eating eggs every day does not inherently lead to weight gain. Eggs can be part of a weight management strategy due to their high protein content, which helps promote feelings of fullness. However, overall caloric intake and lifestyle choices play a significant role in weight management, so it’s essential to consider the entire diet[2][4].