Table of Contents
We all know eggs are nutritious, but did you know how you cook eggs drastically affects their health benefits? Discover the best ways to cook eggs to preserve those valuable nutrients, especially lutein and zeaxanthin for eye health.
How to Cook Eggs for Maximum Benefits
To get the most antioxidant power from your eggs, especially those amazing carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin, remember this: gentle heat is key.
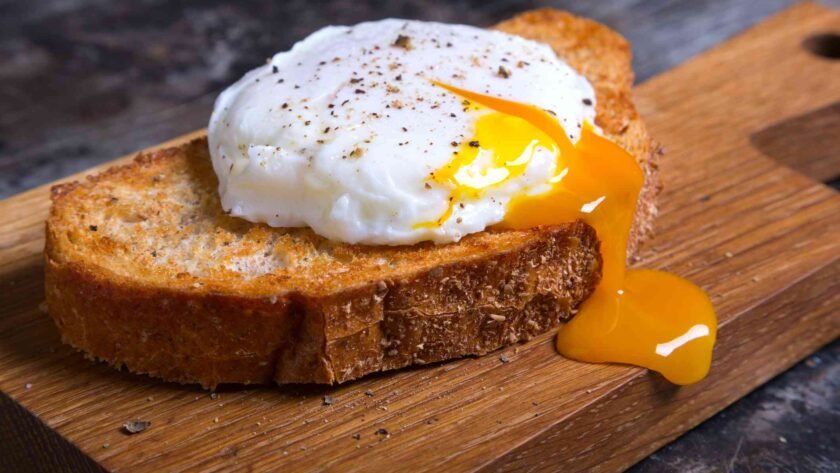
Here’s the trick: you want to cook the whites thoroughly, but keep that yolk runny and delicious.
- Think sunny-side up with a perfectly runny yolk.
- Soft-boiled eggs are another great option.
- Poached eggs, cooked gently in simmering water, are perfect too.
- Even scrambled eggs can work if you cook them lightly and avoid overcooking.
Why so gentle? Lutein and zeaxanthin are sensitive to heat, so the less you blast them, the more your body benefits!
So let’s dive into the details…
How to Cook Eggs for Maximum Antioxidant Nutrients
So, let’s talk about the best way to prepare your eggs for maximum nutrition, and I’m mainly talking about the carotenoids in the eggs: lutein and zeaxanthin.
- This section focuses on maximizing the nutritional value of eggs, specifically the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin.
What are Lutein and Zeaxanthin?
Both of these are very powerful compounds in certain foods that have very unique health benefits. They’re in vegetables, egg yolks, shrimp, lobster, salmon, and there’s quite a few others. It’s in avocados, but these two specific compounds accumulate mostly in the eye.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin are powerful compounds found in various foods, including egg yolks.
- These compounds are particularly beneficial for eye health.
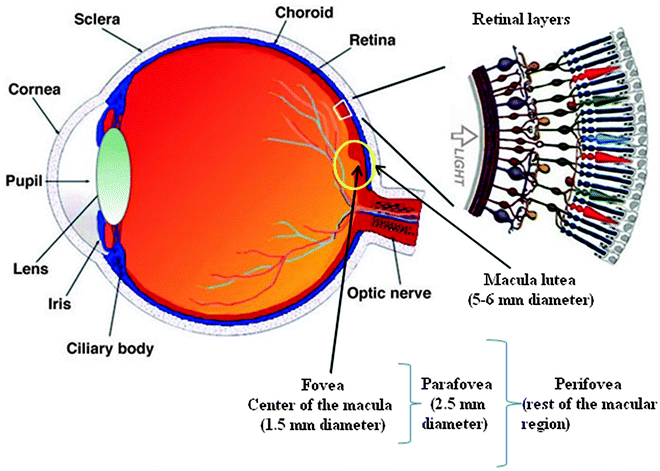
They also go into the liver and certain parts of your brain, but most of it goes into the eye – part of the retina, which is the extension of the brain. It’s all neurological tissue, and the back part, the center part, it’s called the macula, and also in the lens of the eye.
Benefits of Lutein and Zeaxanthin

So both of these compounds can help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration as well as cataracts.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin primarily accumulate in the macula and lens of the eye.
- They help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
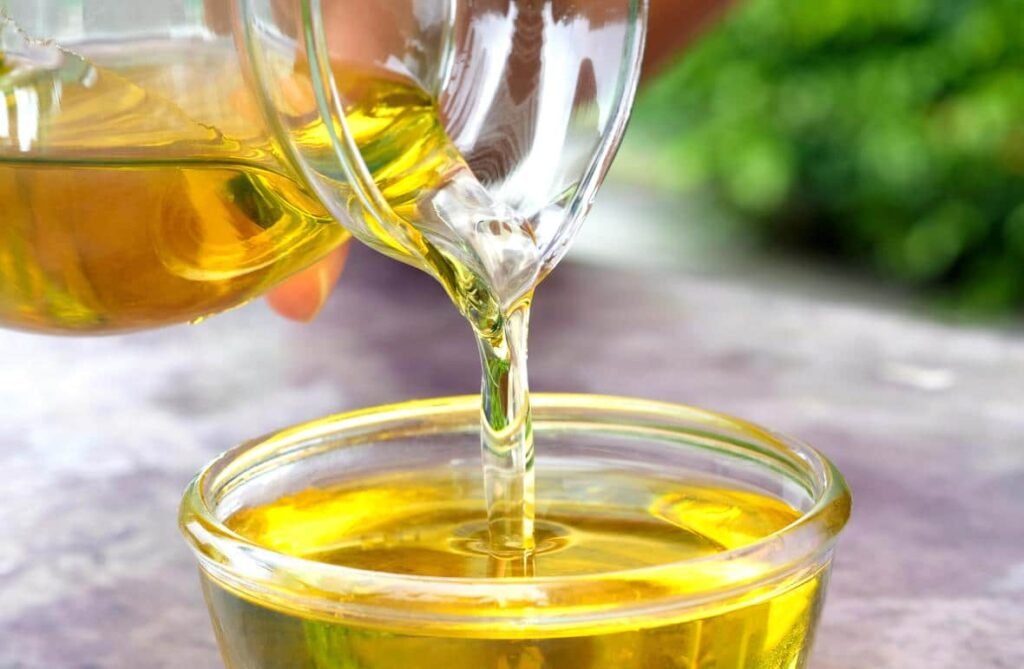

Now, I would also recommend avoiding things that cause inflammation, specifically vegetable oils: soy, corn oil, canola, and cottonseed oil.
Those are very inflammatory, and they create a lot of free radical damage, creating destruction to your tissue.
So, the combination of avoiding the omega-6 fatty acids and consuming foods high in these two compounds can help decrease the risk of damage to your macula as well as your lens.
Avoid These Oils
- Avoid inflammatory oils like soy, corn, canola, and cottonseed oil, as they can contribute to eye damage.
- Reduce omega-6 fatty acid intake to further protect eye health.
How Lutein and Zeaxanthin Help the Eyes
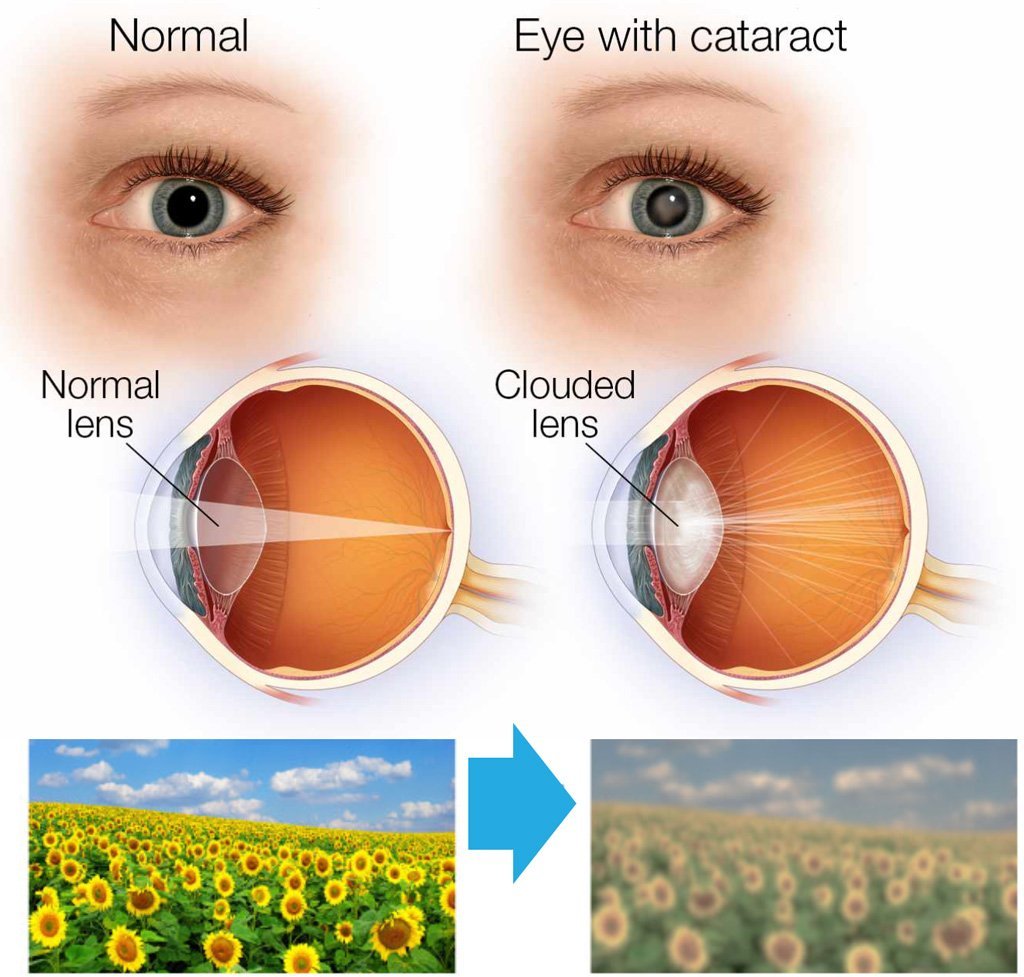
Now, with a cataract, things are going to be cloudy, okay? Like an opaque type of cloudiness on the eye. But if there’s degeneration in the macula, you’re going to lose vision in the central part as well as things are going to be less defined. These two compounds also prevent the blue light; they filter out blue light. They actually absorb the blue light, and so that’s another benefit. Also, they’re anti-inflammatory; they’re very powerful antioxidants.
- Cataracts cause cloudy vision, while macular degeneration affects central vision.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin act as antioxidants and filter out harmful blue light.
The Best Way to Cook Eggs for Nutrients
So now that you understand the power of these two chemicals and eggs, how do you maximize nutrition? How do you prepare your eggs? Well, they’re very sensitive to heat, so the less you heat them the more nutrition you’re going to have.
- Heat can degrade lutein and zeaxanthin, so it’s best to cook eggs with minimal heat.

So, like if you’re going to fry an egg over easy so the yolk is runny, if you’re going to boil an egg, don’t overcook it, poached eggs are really good, if you’re going to scramble the egg just try not to overcook it too much.
- Cooking methods that preserve the yolk’s runny consistency are ideal.
- Examples include over-easy eggs, soft-boiled eggs, poached eggs, and lightly scrambled eggs.
Raw Eggs?

Now, should you consume raw eggs? Now, the problem with that is when you consume raw egg whites, it can deplete other nutrients like biotin.
So, I recommend cooking the white part, but leave the yolk runny.
- Consuming raw egg whites can interfere with biotin absorption.
- It’s recommended to cook the egg whites while keeping the yolk runny.
- Opt for pasture-raised organic eggs for optimal nutrition.
Summary
I’m primarily focusing on two powerful compounds called lutein and zeaxanthin. These two carotenoids are found in vegetables, egg yolk, shrimp, lobster, salmon, and avocados.
Lutein and zeaxanthin mostly accumulate in the eyes. They can help reduce the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts.
As a side note, to further reduce your risk of these issues, avoid inflammatory oils, including vegetable oils, soy oil, corn oil, cottonseed oil, and canola oil. These can cause a lot of free radical damage that destroys healthy tissue.
Lutein and zeaxanthin help the eyes by:
- Filtering out blue light
- Reducing inflammation
- lowering free radicle damage
The best way to preserve the vital nutrients in your eggs is to cook them with a runny yolk. The less you heat the yolk, the more nutrients they contain. Try not to overcook hard-boiled eggs. If you scramble your eggs, try not to cook them too much.
The problem with raw eggs is that the uncooked egg whites can deplete other nutrients like biotin. So always cook the whites, but leave the yolk runny.
Always choose pasture-raised, organic eggs.
DATA
FAQ
What is the best way to cook eggs for health?
The best way to cook eggs for health is to boil them. Boiling eggs preserves most of their nutrients and antioxidants, such as choline, which is important for brain health[2][8]. Boiled eggs also have a higher protein content compared to other cooking methods[11]. Additionally, boiling eggs eliminates the need for added fats or oils, keeping the calorie count low and making them a healthier choice.
How to eat an egg for the maximum benefit?
To get the maximum benefit from eating eggs:
- Choose boiled eggs over other cooking methods like frying, which can add unhealthy fats[2][11].
- Consume eggs as part of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Pair eggs with foods high in vitamin C, such as bell peppers or tomatoes, to enhance the absorption of the eggs’ nutrients.
- Opt for eggs enriched with omega-3 fatty acids or antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin for added health benefits[8][10].
- Consume eggs in moderation as part of a healthy lifestyle and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations.
What is the best way to cook eggs for max protein?
Boiling eggs is the best way to cook them for maximum protein retention. Boiling preserves more of the egg’s natural protein content compared to frying or scrambling, which can cause some protein denaturation[11]. To get the most protein from boiled eggs:
- Use fresh, high-quality eggs.
- Bring the water to a rolling boil before gently adding the eggs.
- Cook the eggs for 10-12 minutes for hard-boiled eggs.
- Immediately transfer the cooked eggs to an ice bath to stop the cooking process and make them easier to peel.
- Consume the boiled eggs as soon as possible for optimal protein absorption.
How do you boil eggs for maximum protein?
To boil eggs for maximum protein:
- Place the eggs in a single layer in a saucepan and cover with cold water by 1 inch.
- Bring the water to a rolling boil over high heat.
- Once the water reaches a boil, remove the pan from the heat and cover with a lid.
- Let the eggs sit in the hot water for 10-12 minutes for hard-boiled eggs.
- Drain the hot water and cover the eggs with cold water or transfer them to an ice bath to cool.
- Peel the eggs and enjoy them as a high-protein snack or incorporate them into your meals.
Is boiled egg healthy?
Yes, boiled eggs are a healthy food choice. They are:
- High in protein, with one large egg containing about 6 grams of high-quality protein[11].
- Rich in essential nutrients like choline, which is important for brain health[2][8].
- Low in calories, with one large boiled egg containing only about 78 calories.
- Free from added fats or oils, making them a healthier option compared to fried eggs.
- Easy to digest and versatile, allowing for easy incorporation into various diets and recipes.
However, it’s important to consume eggs in moderation as part of a balanced diet and to consider individual health factors and dietary needs.
Do eggs keep better raw or boiled?
Boiled eggs keep better than raw eggs. Here’s why:
- Boiling eggs extends their shelf life: Boiled eggs can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 1 week, while raw eggs typically last 3-5 weeks in the shell[6].
- Boiling kills bacteria: The high heat of boiling helps kill any harmful bacteria present on the egg’s shell or inside the egg, making boiled eggs safer to consume[6].
- Boiling makes eggs easier to peel: Boiled eggs are easier to peel and less likely to stick to the shell compared to raw eggs.
- Boiling changes the egg’s structure: The heat from boiling denatures the egg’s proteins, changing their structure and making them less susceptible to bacterial growth.
However, it’s important to store boiled eggs properly in the refrigerator and consume them within a week for optimal freshness and safety.
Why is it better to boil eggs?
There are several reasons why boiling eggs is better:
- Boiling preserves more nutrients: Boiling eggs helps retain more of their natural nutrients, such as choline and vitamins, compared to frying or scrambling[2][8].
- Boiling requires no added fats: Boiling eggs doesn’t require the addition of oils or butter, keeping the calorie count low and making them a healthier choice[11].
- Boiling is a simple cooking method: Boiling eggs is a straightforward process that doesn’t require much time or effort, making it a convenient option for busy schedules.
- Boiled eggs are versatile: Boiled eggs can be easily incorporated into various dishes, such as salads, sandwiches, or as a standalone snack.
- Boiling is cost-effective: Eggs are an affordable source of protein, and boiling is a cost-effective way to prepare them.
However, it’s important to note that while boiling is generally considered the healthiest way to cook eggs, they should still be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Which is healthier, poached or boiled eggs?
Both poached and boiled eggs are healthy options, but boiled eggs may have a slight advantage:
- Boiled eggs retain more nutrients: The high heat of boiling helps preserve more of the egg’s natural nutrients, such as choline and vitamins[2][8].
- Boiled eggs have a longer shelf life: Hard-boiled eggs can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 1 week, while poached eggs have a shorter shelf life[6].
- Boiling is a simpler cooking method: Boiling eggs requires less hands-on time and effort compared to poaching.
However, poached eggs also offer benefits:
- Poached eggs have a softer texture: Some people prefer the delicate, soft texture of poached eggs over the firmer texture of boiled eggs.
- Poached eggs may be easier to digest: The gentle cooking method of poaching may make the eggs easier to digest for some individuals.




