Table of Contents
Discover Why is potassium important for your health. Learn about its vital roles in cellular energy, muscle function, nerve conduction, and pH regulation. Explore symptoms of potassium deficiency and find out which foods are rich in this essential mineral.
Potassium is an often overlooked but essential mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining optimal health. From cellular energy production to muscle function and nerve conduction, potassium is involved in numerous physiological processes. In this article, we will delve into the importance of potassium, exploring its key roles in the body.
We will also discuss the symptoms of potassium deficiency and provide insights into dietary sources that can help you maintain adequate potassium levels. Discover why potassium is a crucial nutrient for overall well-being and how you can ensure you’re getting enough of it in your diet.
Why is potassium important

We’re gonna talk about a very important mineral , potassium .
Why is it so important ?
Well , number 1 because we need so much of it .
Out of all the nutrients , vitamin a , vitamin b , calcium , magnesium , potassium being a mineral is needed in large amounts .
I’m talking 40 700 milligrams .
Because it’s used in all the cellular reactions .
It’s also used to store your sugar in your liver and your muscle .
Now let’s explain what I mean by that .
Stored sugar is a good thing .
What is glycogen
We need to store some sugar , to be able to handle a quick release of energy and glucose being the molecule of sugar , if you stick them together in a group they’re called glycogen .
So glycogen is the storage of glucose .
Mainly in the liver , mainly in the muscles and it’s used like , you know , it’s very instant so you can regulate that .
So we need that .It just so happens potassium is the mineral that allows glucose to be stored as glycogen So for every glucose molecule you need 1 potassium molecule or element .
So that’s 1 thing .So let’s say you’re deficient in potassium .
That means you’re not gonna store the glucose as well .
So if you don’t store glucose , your body then stores more fat .
So that’s interesting . So a couple other points .
Where to get potassium
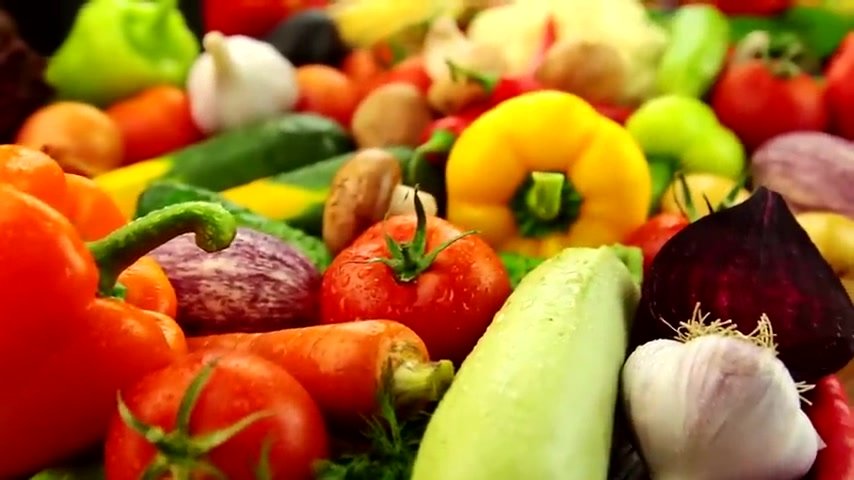

Where do you get your potassium ?
Mainly from vegetables but you can even get it from animal proteins as well .
But , you know , like the greens , leafy greens , beet tops are really high , avocados are very , very large amounts in avocados .
how do we know we’re getting enough potassium ?

Well , 1 cup of greens , vegetable , or , salads on average equal , 1 ounce .
1 cup equals 1 ounce and you need 47100 so you’re gonna you’re gonna need about between 8 10 ounces or 8 , 7 well actually 7 to 10 cups okay or 7 to 10 ounces .
That would be like 1 of those salad containers or bags of salad that you see at the grocery store .
Just need 1 of those per day .
It’s not too much .
When you take a cup of salad , I’m not talking about , like , pack it down extremely tight .
Just kind of , like , put it in there like a good handful .
That’s like 1 cup or 1 ounce .
How much potassium to consume
You need at least 7 up to 10 .
I consume more than that . I consume probably 20 .
So it doesn’t hurt if you have more because the kidneys will also get rid of anything that’s too much , especially when it comes down to potassium .
A lot of people supplement Potassium because it’s hard to get the Potassium and they get it straight into the body and also in certain conditions , you need more potassium to improve these conditions .
1 is rheumatoid arthritis . Big time .
You go up into the 6000 , 7000 milligrams you can really put those symptoms in remission .
Insulin resistance

Another 1 is diabetes or insulin resistance .
Why ?
Because insulin does control .
It’s like the door that allows insulin , potassium to go in the cell .
So insulin controls level of potassium and , when you have insulin resistance , you can’t pull that potassium in the cell .
So if you don’t pull potassium in the cell , you have a lot of problems .
To make a long story short , and make it really simple , if you increase more potassium in the diet , you decrease the stress on the insulin dysfunction .
You decrease the need for insulin .
So having a little more will actually help insulin resistance and diabetes.
So they both work kind of like a teeter totter .
If you have enough potassium you won’t have sugar cravings .
Why ?
Because you’re gonna store the sugar and you’re gonna your body gonna you’re gonna have better blood sugar levels because potassium stabilizes blood sugars so you don’t have this dip down .
So potassium helps blood sugars , insulin dysfunction and cravings for sweets .
If you crave for sweet , we know you’re potassium deficient .So we need more potassium .
When I consume a meal I always have the vegetable first , not at the end of the meal .
Because I’ve experimented .
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Importance of Potassium | Needed in large amounts (40,000-70,000 milligrams), used in all cellular reactions, and necessary for storing sugar as glycogen |
| Glucose Storage | 1 potassium molecule needed for every glucose molecule to be stored as glycogen |
| Potassium Deficiency | May result in poor glucose storage and increased fat storage |
| Sources of Potassium | Mainly from vegetables, but also from animal proteins |
| Daily Potassium Intake | At least 7-10 cups of vegetables or 7-10 ounces of salad |
| Conditions Requiring More Potassium | Rheumatoid arthritis, insulin resistance or diabetes |
| Benefits of Increased Potassium | Decreased stress on insulin dysfunction, improved insulin resistance and diabetes, decreased sugar cravings, and stabilized blood sugar levels |
| Potassium-Sodium Ratio | Ideal ratio is 4:1, but most people have too much sodium and not enough potassium |
| Ketogenic Diet and Potassium | Replenishing potassium levels is important to avoid dehydration |
| Potassium Depletion | Consuming sugar and refined carbohydrates can deplete potassium levels and cause fluid retention |
If I do the protein first I tend to will keep eating more and more protein .

There’s like no turn off switch versus the vegetable first which gives me the potassium and it kinda turns off that hunger and I don’t eat as much protein .
My son , for example , he’ll sit down and eat chicken wings .
He can eat , I’m talking like massive quantities .
So I get him to have the vegetable first and then he doesn’t need as much protein cause we just need like 3 to 6 ounces .
So I always have the vegetable first for that reason .
When you consume potassium , you help get , you balance the sodium .
So we need this potassium sodium ratio .
So we need 4 times as much potassium as sodium and that’s why we need this .
Most people have way too much sodium and not enough potassium .
So they’re gonna retain fluid .
When you have low potassium , you retain fluid and you’re salt sensitive , high blood pressure .
If you take potassium your blood pressure comes right down .
Probably is in in many cases the cause of high blood pressure , low potassium .
Now as you do a ketogenic diet that’s real low carbs .
It’s low carbs and you’re gonna dump a lot of fluid .

Because 1 of the things 1 1 thing is that with carbs especially refined carbohydrates , sugars cause retention of fluid .
Because when you consume carbohydrate you also deplete your potassium .
So when you have like cakes and cookies and sugar and donuts and breads and pasta , you’re automatically depleting the potassium .
Now why is that ?
Well because in nature , sugarcane is probably 1 of the 1 of the highest things with potassium that you could consume .
Not 1 of the highest , but it’s very very high .

So there’s a lot of potassium in sugarcane , but what they do is they refine it and they get rid of the potassium and other minerals like iron into molasses and they put as white refined sugar and brown sugar as a really depleted potassium deficient sweetener .
When you consume this refined sweetener over here without the mineral , you tend to your body almost like starts to plea it’s a potassium depleter .
It’s almost like your body will start , trying to recombine that glucose with sugar and starts pulling from reserves .
So in other words , to make a long story short , when you consume sugar , I’m trying to make this really simple , when you can term refined sugar , junk food , you’re depleting your potassium and you’re you’re increasing your sodium and you’re increasing your fluid retention .
So when we cut that out , you dump a lot of fluid .
So you can you can drop a lot of weight in 1 week .
That’s good , but you better put your potassium back in there because , if you’re dumping a lot of fluid , you need to put the , the hydration back in there so you have the volume of fluid , not just water .
You need the electrolytes , that help the connectivity .

So when people do the ketogenic diet and they feel really tired , boy you just need to add a little potassium and boom the energy comes up , sometimes a little sodium .
Even with low blood pressure , you know , you need potassium and sodium to help get more fluid in there , not just water .
So our bodies need fluid .So I wanted to just give you an overview of potassium and what it can do and how important it is . So make sure you eat your vegetables on this program .
key Points
- Potassium is a mineral that is needed in large amounts in the body, between 40,000-70,000 milligrams.
- It is used in all cellular reactions and is necessary for storing sugar in the liver and muscles as glycogen.
- For every glucose molecule, one potassium molecule is needed to store it as glycogen.
- If someone is deficient in potassium, they may not store glucose as well and may store more fat instead.
- Potassium can be found mainly in vegetables, but also in animal proteins.
- To ensure you are getting enough potassium, you should consume at least 7-10 cups of vegetables or 7-10 ounces of salad per day.
- Certain conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and insulin resistance or diabetes may require higher levels of potassium.
- Increasing potassium in the diet can help decrease the stress on insulin dysfunction and improve insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Consuming vegetables first in a meal can help turn off hunger and reduce the need for protein.
- A potassium-sodium ratio of 4:1 is ideal, but most people have too much sodium and not enough potassium.
- Consuming sugar and refined carbohydrates can deplete potassium levels and cause fluid retention.
- When starting a ketogenic diet, it is important to replenish potassium levels to avoid dehydration.
DATA
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Potassium-HealthProfessional
FAQ
What happens if you don’t get enough potassium?
When you don’t get enough potassium, it can lead to various health issues. Some potential consequences of potassium deficiency include increased blood pressure, depletion of calcium in bones, and an increased risk of kidney stones
What food is highest in potassium?
Several foods are rich in potassium. Some of the highest potassium sources include:
- Dried apricots
- Prunes
- Raisins
- Orange juice
- Bananas
- Acorn squash
- Potatoes
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Broccoli
- Lentils
- Kidney beans
- Soybeans
- Nuts
- Milk and yogurt
- Meats, poultry, and fish
Why is potassium of primary importance to the human body?
Potassium is of primary importance to the human body because it plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. It is necessary for proper kidney and heart function, muscle contraction, and nerve transmission. Potassium helps maintain fluid balance, regulate blood pressure, support proper muscle and nerve function, and promote overall cardiovascular health
Does potassium give you energy?
While potassium itself does not directly provide energy, it is essential for maintaining proper muscle function and nerve transmission. By supporting these processes, potassium indirectly contributes to overall energy production and helps prevent muscle weakness and fatigue
Why is potassium important for the heart?
Potassium is vital for the heart’s proper functioning. It helps regulate the heart’s electrical activity, ensuring a regular heartbeat. Adequate potassium levels can help maintain a healthy heart rhythm and prevent conditions such as arrhythmias and heart palpitations
Which food is highest in potassium?
Some of the highest potassium-rich foods include:
- Dried apricots
- Prunes
- Raisins
- Orange juice
- Bananas
- Acorn squash
- Potatoes
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Broccoli
- Lentils
- Kidney beans
- Soybeans
- Nuts
- Milk and yogurt
- Meats, poultry, and fish
What are 5 benefits of potassium?
Potassium offers several benefits to the body, including:
- Regulating blood pressure: Adequate potassium intake can help lower blood pressure levels.
- Supporting heart health: Potassium helps maintain a regular heartbeat and prevents heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Promoting muscle function: Potassium is essential for proper muscle contraction and preventing muscle weakness.
- Enhancing nerve transmission: Potassium plays a role in transmitting nerve signals throughout the body.
- Supporting bone health: Some studies suggest that higher potassium intake may improve bone mineral density, contributing to stronger bones
What does high potassium do for the body?
While potassium is essential for the body, excessively high levels of potassium (hyperkalemia) can be harmful. Hyperkalemia can disrupt normal heart rhythm, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions. It is important to maintain a balance and avoid excessive potassium intake, especially for individuals with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications
How much potassium per day?
The recommended daily potassium intake varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. Here are the average daily recommended amounts in milligrams (mg):
- Adults 19+ years (men): 3,400 mg
- Adults 19+ years (women): 2,600 mg
- Pregnant women: 2,900 mg
- Breastfeeding women: 2,800 mg
It is important to note that individual needs may vary, and it is best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations
Potassium benefits for muscles
Potassium is essential for proper muscle function. It helps regulate muscle contractions, including those of the heart. Adequate potassium levels can prevent muscle weakness, cramps, and spasms. It also plays a role in maintaining electrolyte balance, which is crucial for muscle health and performance
Potassium sources
- Fruits: Dried apricots, prunes, raisins, oranges, bananas
- Vegetables: Acorn squash, potatoes, spinach, tomatoes, broccoli
- Legumes: Lentils, kidney beans, soybeans
- Nuts
- Dairy products: Milk and yogurt
- Meats, poultry, and fish
- Salt substitutes (Note: Consult with a healthcare provider before using salt substitutes, especially if you have kidney disease or take certain medications)
Potassium benefits for skin
While potassium is primarily known for its role in overall health, it can indirectly benefit the skin. Potassium helps maintain proper hydration and fluid balance in the body, which can contribute to healthy skin. Additionally, potassium-rich foods, such as fruits and vegetables, often contain other beneficial nutrients that support skin health, such as vitamins and antioxidants



