Table of Contents
Are you experiencing fatigue, hair loss, or skin problems? Could Zinc Deficiency be the culprit? This article explores the common signs and symptoms of Zinc Deficiency, as well as its causes and solutions. Learn how to recognize the subtle clues your body might be giving you and discover if Zinc Deficiency is impacting your health. Read on to find out more about this essential mineral and how to address potential it
Brief The Article:
What is Zinc and Why is it Important?
- Zinc is a trace mineral, meaning your body only needs small amounts, but it’s crucial for various bodily functions.
- Zinc deficiency can lead to a wide range of health problems.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
- Loss of smell and taste
- Decreased appetite
- White spots on nails
- Skin issues like acne, eczema, and dermatitis
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Increased susceptibility to rhinovirus infections (common cold)
- Low testosterone and libido
- Mouth ulcers
What Causes Zinc Deficiency?
- Diets low in zinc-rich foods
- High carbohydrate intake (sugar depletes zinc)
- Phytic acid in grains (inhibits zinc absorption)
- Low stomach acid (hinders zinc absorption)
- Stress (depletes zinc reserves)
Who is at Risk of Zinc Deficiency?
- People with poor diets
- People with digestive issues (low stomach acid, etc.)
- People under high stress
- People in developing countries with limited access to nutrient-rich foods
How to Address Zinc Deficiency?
- Eat a diet rich in zinc-rich foods like oysters, red meat, and poultry.
- Consider supplementing with zinc, but be mindful of dosage and potential interactions with other minerals like copper.
- Address underlying health issues that may contribute to poor zinc absorption (e.g., low stomach acid).
So let’s dive into the details…
Zinc Deficiency: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions
In this topic, we’re going to talk about zinc deficiency. Now, what is zinc? Zinc is a trace mineral.
It’s basically a mineral that’s needed in a lot smaller amounts, but it’s necessary because if you’re deficient you’re going to have a lot of different issues.
- Zinc is a trace mineral needed in small amounts.
- Zinc deficiency can lead to various health problems.
Common Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
Number one, your sense of smell will go away. Your sense of taste will not be there. You won’t actually be as hungry. Those are some common symptoms.
White spots on the nails. You got these little uh spots in the nail but but usually what happened is that you ate a lot of carbohydrate that depleted the zinc because too much sugar or carbohydrate will pull zinc out of your body.
- Zinc deficiency symptoms include:
- Loss of smell
- Loss of taste
- Decreased appetite
- White spots on nails (often linked to high carbohydrate intake and resulting zinc deficiency)
Zinc Deficiency and Skin Health: The Connection
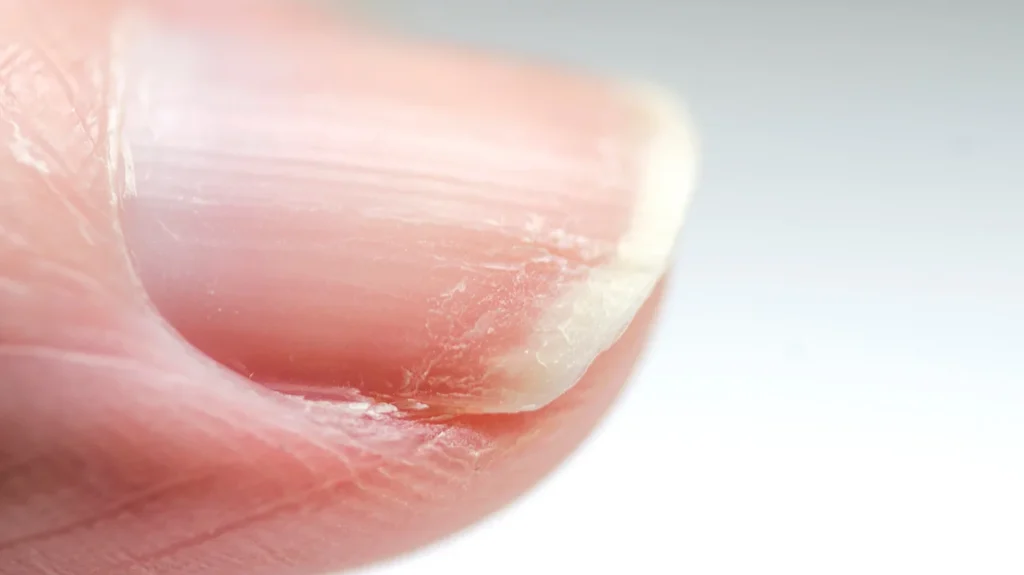
So if you had a little white speck on the middle of your nail, and by the way, the nail grows every six months, we know about three months ago you had a birthday party and you ate the whole cake right? So that’s one way of determining that.
Okay now we have acne, skin issues, eczema, all these skin issues, dermatitis could be related to zinc. But there’s other things that can cause skin issues too that almost mimic a zinc deficiency, like a vitamin A deficiency or a vitamin B2 or B6 deficiency.
- White spots on nails can indicate past instances of zinc deficiency (e.g., due to high sugar consumption).
- Skin issues like acne, eczema, and dermatitis can be linked to zinc deficiency.
- Other vitamin deficiencies (A, B2, B6) can cause similar skin problems.
Zinc and Vitamin A
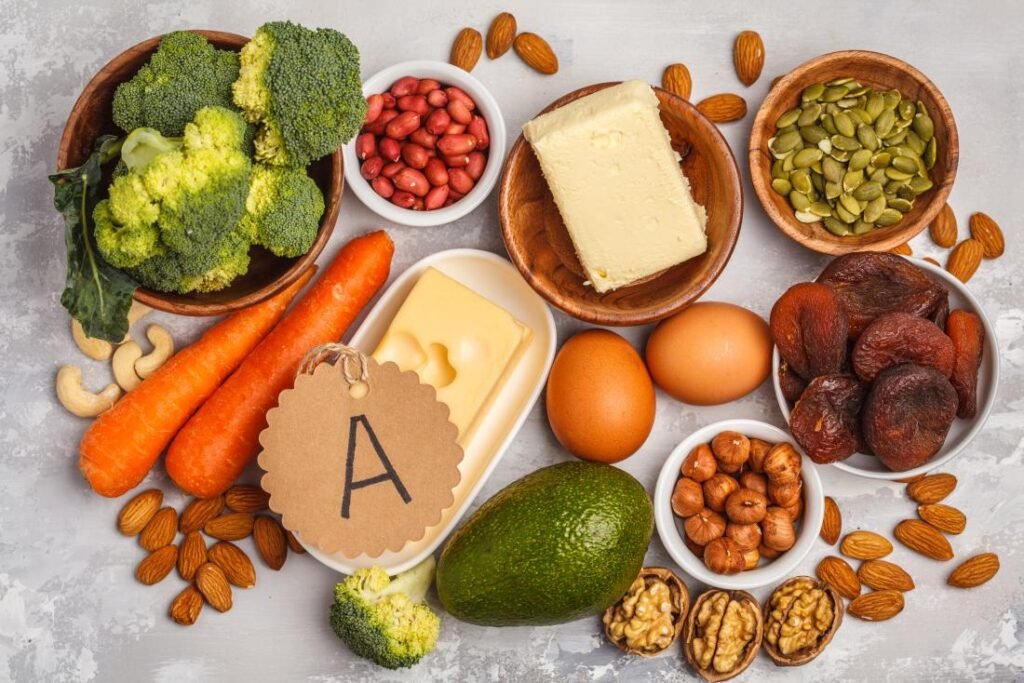

So really you have to look at all of these things to see what it is. But I will say that if you’re low in zinc, you can’t absorb or utilize vitamin A.
So they always work together, like minerals work with vitamins together and zinc is kind of like a a main uh mineral that’s used in over 300 enzymes, so it’s in a lot of chemical body reactions okay, so with proteins.
- Proper diagnosis of zinc deficiency requires considering other potential deficiencies.
- Zinc deficiency can hinder vitamin A absorption and utilization.
- Zinc is a key component of over 300 enzymes, highlighting its importance in various bodily processes.
Zinc Deficiency and Hair Loss

And that’s brings us to this one down here with hair, alopecia, which is like little spots of hair growth that’s gone or thinning hair that could be a B vitamin deficiency like biotin, but it can also be a zinc deficiency as well, they work together.
- Hair loss (alopecia) can be a symptom of zinc deficiency.
- Zinc deficiency and B vitamin deficiencies (like biotin) can both contribute to hair loss.
Zinc and Rhinoviruses:
Okay then we have rhinoviruses. Well, zinc being a trace mineral helps put uh viruses back in remission. Now the thing about viruses is you can’t kill a virus because it’s not alive.
It’s a piece of genetic material that’s wrapped in a sack that can activate your own energy from your cells and create a cascade of an immune response.
So zinc is one that’s specific to actually keep the rhinovirus in check and actually it can if you take zinc when you’re starting to get sick it can speed up the time of overcoming the sickness and actually can prevent that issue as well.
But rhinovirus is like the one that you have the postnasal drip, the sinus congestion, the sore throat, the sneezing um so you need more um zinc.
- Zinc can help manage rhinovirus infections.
- Taking zinc at the onset of illness can potentially speed up recovery and even prevent some viral infections.
- Rhinovirus symptoms include postnasal drip, sinus congestion, sore throat, and sneezing.
- Adequate zinc levels are important for fighting off rhinoviruses.
Zinc Deficiency and Hormone Health: The Impact on Testosterone
All right then we have lower testosterone, both in male and female. If you have low testosterone, your libido will be very low. Okay that can come from a zinc deficiency.
- Low testosterone in both men and women can be linked to zinc deficiency.
- Zinc deficiency can contribute to low libido.
Stress, and Mouth Ulcers: Understanding the Connections
Um and then mouth ulcers again that can come from other things, but that little um sore on the inside of the mouth which is usually virus-related, the viruses like herpes come out of remission if you’re under stress and because the zinc becomes deficient.
So sugar and stress will deplete the zinc reserves. Okay because more cortisol pumps out and then it needs zinc to to use the for the immune system and then basically you deplete your zinc reserves.
- Mouth ulcers can be a sign of zinc deficiency, often exacerbated by stress.
- Stress and sugar consumption can deplete zinc reserves.
- The body requires zinc to manage stress and support the immune system.
Dietary Sources and Factors Affecting Absorption

So it’s involved in a lot of different enzymes um now it’s in oysters that has a lot of zinc um from the sea of course and then we it’s in uh animal like beef. It’s in pork, it’s in red meat. It’s also in seal.
It’s in a lot of foods but it’s really high in these foods right here and also zinc actually helps make the red white blood cell.
So the adrenal gland uh controls the white blood cell, it suppresses the immune system and that’s uh and zinc is involved in that whole process.
So we have a relationship between countering stress, having the trace minerals to make sure that your immune system is strong.
| Food Source | Zinc Content |
|---|---|
| Oysters | High |
| Beef | Moderate |
| Pork | Moderate |
| Shellfish | Moderate to High |
- Zinc is found in various foods, with oysters, beef, pork, and red meat being particularly rich sources.
- Zinc plays a role in red and white blood cell production.
- Zinc is important for stress management and immune system function.
Zinc Deficiency in Developing Countries: A Serious Concern
Okay so here just and lastly I want to talk about um in other countries like not in America but third world countries a lot of children and infants will die because of a zinc deficiency
because they have diarrhea and so you know zinc is, unfortunately, they don’t put it back in the soils so it could be a factor of it’s either not in your food because it’s not in the soil,
it could be you’re trying to get your zinc from grains but not if there’s a certain inhibitor for zinc and other minerals called phytic acid in grain. So that chemical in the grain naturally prevents the absorption of minerals okay.
- Zinc deficiency is a serious issue in developing countries, contributing to infant and child mortality.
- Soil depletion can lead to zinc deficiency in food crops.
- Phytic acid in grains can inhibit zinc absorption.
Factors Affecting Zinc Absorption and Contributing to Zinc Deficiency

And then also your if your stomach acid is not strong enough you’re not going to pull that acid in to so if you have heartburn you have gird indigestion chances are you’re zinc deficient just from that alone.
- Insufficient stomach acid can hinder zinc absorption.
- Conditions like heartburn and GERD can contribute to zinc deficiency.
Okay so there’s a lot of different aspects of zinc I wanted to cover uh some of them but there’s a lot more but I hope this helped and I will see you in the next topic!
- Zinc deficiency is a multifaceted issue with various contributing factors.
- Understanding zinc deficiency is crucial for maintaining optimal health.
additional-resources
FAQ
What is the most likely symptom of a zinc deficiency?
The most common symptom of zinc deficiency is a weakened immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections. However, other early signs may include loss of appetite, impaired taste (hypogeusia), and slow wound healing. It’s important to note that symptoms can vary from person to person.
What are the major problems of zinc deficiency?
Zinc deficiency can lead to several significant health issues:
- Impaired immune function
- Delayed growth and development in children
- Reproductive problems in both men and women
- Skin disorders, including acne and eczema
- Cognitive impairment and mood disorders
- Poor wound healing
- Hair loss
- Decreased sense of taste and smell
What are the behaviors of zinc deficiency?
Zinc deficiency can manifest in various behavioral changes:
- Irritability and mood swings
- Lethargy and fatigue
- Decreased appetite
- Impaired concentration and memory
- Depressive symptoms
- Hyperactivity in some cases, especially in children
- Sleep disturbances
What are the oral manifestations of zinc deficiency?
Zinc deficiency can affect oral health in several ways:
- Altered taste perception (dysgeusia)
- Burning mouth syndrome
- Oral ulcers or canker sores
- Periodontal disease
- Delayed wound healing in the oral cavity
- Increased risk of oral infections
- White coating on the tongue (in severe cases)
Signs of zinc deficiency in females
Females may experience specific signs of zinc deficiency:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Fertility issues
- Pregnancy complications
- Hair loss or thinning
- Brittle nails
- Acne or other skin problems
- Decreased libido
- Mood swings and depression
Zinc deficiency symptoms skin
Zinc plays a crucial role in skin health. Deficiency can lead to:
- Acne or worsening of existing acne
- Eczema or dermatitis
- Slow wound healing
- Dry, rough skin
- Rashes or skin lesions
- Cracked or peeling skin, especially on hands and feet
- Increased susceptibility to sunburn
Zinc deficiency neurological symptoms
Zinc is important for neurological function. Deficiency may cause:
- Cognitive impairment and poor memory
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood disorders, including depression and anxiety
- Altered sensory perception (taste, smell)
- Headaches
- In severe cases, seizures or tremors
- Potential link to neurodegenerative diseases
Treatment of zinc deficiency
Treating zinc deficiency typically involves:
- Dietary changes to include more zinc-rich foods
- Zinc supplements (under medical supervision)
- Addressing underlying medical conditions that may cause deficiency
- Lifestyle modifications to improve zinc absorption
- Regular monitoring of zinc levels
- In severe cases, intravenous zinc supplementation
- Balancing zinc intake with other nutrients, especially copper
Zinc and iron deficiency symptoms
Zinc and iron deficiencies often co-occur and share some symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin
- Weakened immune system
- Hair loss
- Brittle nails
- Difficulty concentrating
- In children, delayed growth and development
Symptoms of zinc deficiency in males
Males may experience specific symptoms of zinc deficiency:
- Low testosterone levels
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased sperm count and quality
- Prostate problems
- Male pattern baldness or thinning hair
- Reduced muscle mass
- Increased risk of male infertility
Zinc deficiency diseases
Zinc deficiency can contribute to or exacerbate various diseases:
- Growth retardation in children
- Hypogonadism in males
- Impaired wound healing
- Immune system disorders
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Chronic diarrhea
- Pneumonia (increased risk, especially in children)
Zinc deficiency face
Facial manifestations of zinc deficiency can include:
- Acne or worsening of existing acne
- Pale or sallow complexion
- Dry, flaky skin
- Dark circles under the eyes
- Premature aging signs, such as fine lines
- Hair loss, including eyebrow thinning
- Redness or inflammation around the nose and mouth
Remember, while these symptoms can indicate zinc deficiency, many can also be caused by other conditions. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.



