Table of Contents
Think you know everything about zinc deficiency? Think again! Today, we’re diving into the surprising and often overlooked symptoms of zinc deficiency that you might be missing. Let’s explore these unusual signs and discover how to ensure you’re getting enough of this essential mineral.
Brief The Article:
What is Zinc and Why is it Important?
- Zinc is an essential trace mineral, meaning the body requires it in small amounts for various functions.
- Zinc is often associated with acne treatment and sun protection, but its role extends far beyond that.
- Zinc deficiency can contribute to various health issues, including loss of taste and smell, slow wound healing, hypogonadism (low testosterone), arthritis, and inflammatory conditions.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency: 7 Unusual Signs You Might Be Missing
- Stretch marks
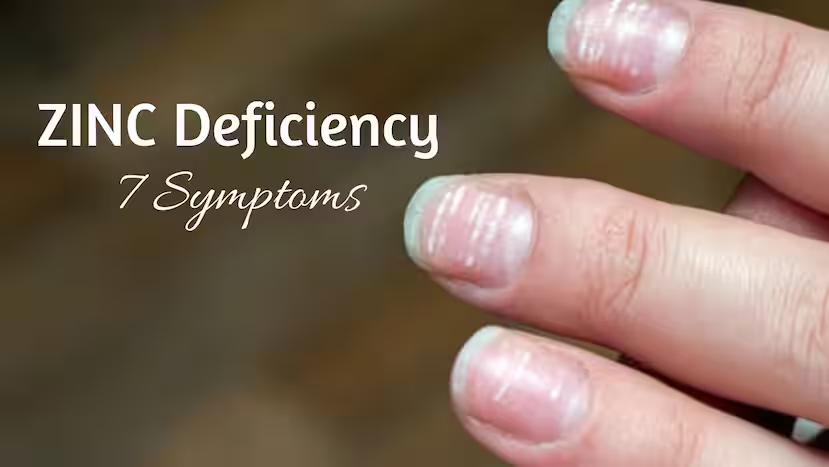
- Poor hair and nail growth, including white spots on nails (which can indicate high carbohydrate consumption three months prior, as sugar depletes zinc).
- High blood pressure
- Cold extremities
- Dwarfism
- Hearing loss
- Zinc deficiency can be caused by poor dietary choices rather than just insufficient intake.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency: Dietary and Lifestyle Factors to Consider
- Foods that can deplete zinc:
- Processed foods
- Refined foods
- Refined grains (due to phytates)
- Whole grains (due to phytates, which bind to zinc and prevent absorption)
- Refined sugar can also hinder zinc absorption.
- Stress can deplete zinc levels.
- Liver damage can impair zinc absorption.
- Colon damage and conditions like diverticulitis and irritable bowel syndrome can also hinder zinc absorption.
The Role of Zinc in the Body
- Zinc acts as a coenzyme, meaning it’s essential for the proper function of many enzymes in the body.
- Zinc is crucial for various bodily processes, including protein synthesis and DNA synthesis.
- Zinc deficiency can have numerous negative health consequences.
- Zinc deficiency primarily affects skin health, immune function, and the lining of the intestines.
Addressing Zinc Deficiency: Food Sources and Testing
- Good sources of zinc:
- Seafood (especially oysters)
- Seaweed
- Fish
- Liver
- Meats
- Animal products
- Vegetables (some)
- Nuts (some)
- It’s important to avoid foods and factors that can deplete zinc levels.
- A zinc taste test can be used to assess zinc deficiency. No taste indicates deficiency, while a strong metallic taste suggests sufficient zinc levels.
- Zinc taste tests are readily available.
Key Takeaway:
Zinc is crucial for various bodily functions, and recognizing the symptoms of zinc deficiency is vital for maintaining optimal health. Ensuring adequate zinc intake through a balanced diet and addressing factors that hinder absorption can significantly impact overall well-being.
So let’s dive into the details…
Introduction to Zinc and Its Importance

So today we’re going to talk about zinc, okay? In the seven weird signs of a zinc deficiency, zinc is a trace mineral which is different than a mineral.
And all that means is you need trace amounts, very small amounts, something usually below a hundred milligrams, but you still need it. It’s very, very essential.
Common Misconceptions About Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency

Most people when they think of a zinc deficiency, they may think of acne because of all the acne creams have zinc in it, or maybe for sunburn to protect you against the UV light.
But it’s also involved with the loss of taste and smell, slow wound healing, hypogonadism (which means that your testicles are smaller and you’re not producing testosterone).
It can come from a zinc deficiency. Arthritis, any inflammatory condition could be a zinc deficiency.
- Zinc deficiency can contribute to various health issues, including:
- Loss of taste and smell
- Slow wound healing
- Hypogonadism (low testosterone)
- Arthritis and inflammatory conditions
Seven Strange Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
But I want to talk about the seven kind of strange symptoms of zinc deficiency that maybe you’ve never heard about:
- Stretch marks could be a zinc deficiency
- Poor hair and nail growth
- White spots on your nails
- High blood pressure could be related to a zinc deficiency
- Cold extremities
- Dwarfism
- Hearing loss as you’re getting older could be a zinc deficiency
Interesting Fact About White Spots on Nails
The white spots on your nails could be a symptom of zinc deficiency, which is interesting because if you see it right in the center and your nail grows every six months,
and it’s right in the center, we pretty much know about three months ago you consumed a lot of carbohydrates.
You may have had a birthday party and you ate the whole cake because that sugar will pull zinc out and it leaves the little white spots.
Causes of Zinc Deficiency

So you could be zinc deficient not necessarily from not eating a certain amount of food, but by eating the wrong foods. Processed foods, refined foods, especially refined grains deplete your zinc.
Whole grains will deplete your zinc because they have something called phytate in the fiber which actually binds with the zinc and you can’t absorb it.
Cooking will dissolve the zinc and it goes out through the water. Refined sugar will actually block the absorption of zinc. Stress will deplete your zinc.
- Foods that can deplete zinc:
- Processed foods
- Refined foods
- Refined grains (due to phytates)
- Whole grains (due to phytates, which bind to zinc and prevent absorption)
Medical Conditions Affecting Zinc Absorption
- Liver damage like in fatty liver, liver that has cirrhosis will block the absorption of zinc
- Colon damage
- Diverticulitis
- Irritable syndrome
The Role of Zinc in the Body
So the core essence of what zinc does, it’s a coenzyme for many, many things in the body, okay? Many chemical reactions. What does that mean?
Coenzyme means that it’s an essential element that makes the enzyme work, and without it, it’s not gonna work. The enzymes do the work of the body
so you can look at zinc as an essential thing that allows something to happen, either approaching to be made or DNA to be synthesized or created. It helps make DNA.
Primary Areas Affected by Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
As you can see, there’s so many different bad effects that can occur if you don’t have enough zinc. The three primary areas that it’ll affect would be:
- Skin – a lot of different skin issues
- Immune system – think about when you start getting run down or cold, usually the cold remedies out there have zinc in them, especially as a preventive action
- The lining of your intestines
How to Get Zinc and Prevent Deficiency
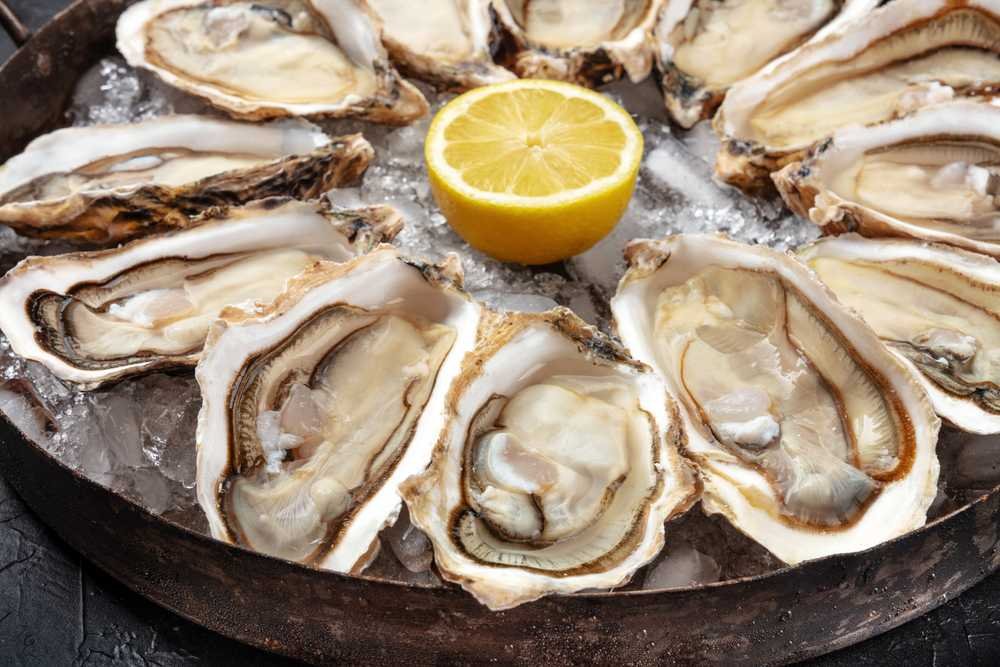

Alright, how do you get zinc? Well, seafood, especially oysters, okay? High in zinc. Seaweed, a very good source of zinc.
Plant-based fish in general, liver like grass-fed liver, meats, animal products. Veggies have some and nuts have some as well. But you also want to avoid the things that deplete the zinc.
- Good sources of zinc:
- Seafood (especially oysters)
- Seaweed
- Fish
- Liver
- Meats
- Animal products
- Vegetables (some)
- Nuts (some)
The Zinc Test: A Simple Way to Check for Deficiency
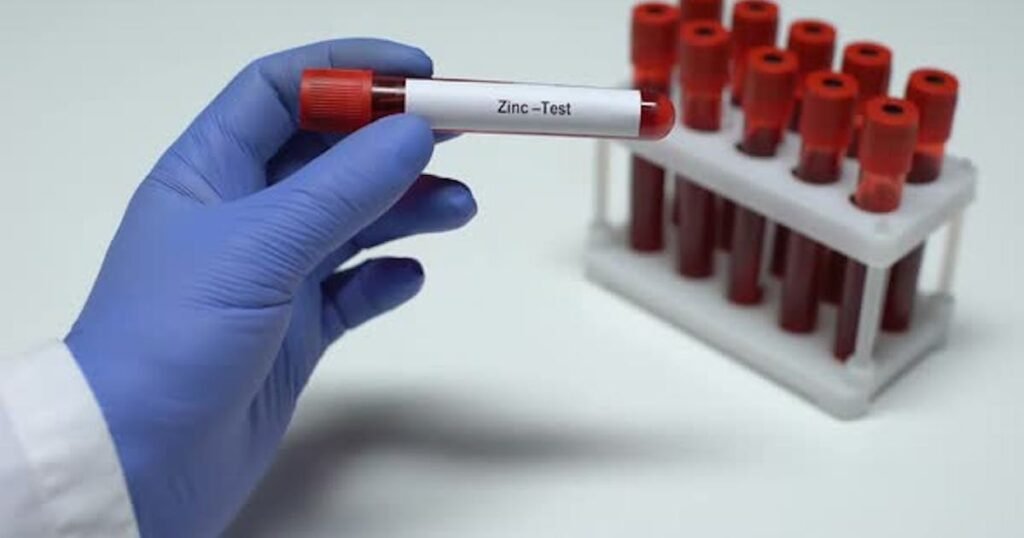
Now lastly, there’s a really cool test that you can get. It’s called a zinc test, and what you do is you put a little bit of zinc on your tongue.
And if you taste nothing, that means you’re deficient in zinc, okay? But if you can taste a very strong metallic taste, that means you have enough zinc.
So it’s a very simple test. I’ll put a couple links down below of different brands that you might want to check out, but it’s a very simple way to do a quick test to see if you’re zinc deficient.
Summary
- What is zinc? Zinc is a trace mineral, which is different from a mineral. Basically, you need trace amounts, but you still need it.
- You can be zinc deficient not only from not eating a certain amount of food but by eating the wrong foods.
More Well Known Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency:
• Acne
• Loss of Taste/Smell
• Slow Wound Healing
• Hypogonadism
• Arthritis
Weird Zinc Deficiency Symptoms:
- Stretch Marks
- Poor Hair / Nail Growth
- White Spots on Nails
- High Blood Pressure
- Cold Extremities
- Dwarfism
- Hearing Loss
Zinc Deficiency Causes:
- Processed Grains
- Whole Grains (Phytates)
- Cooking
- Sugar
- Stress
- Liver / Colon Damage
Zinc Function:
• A coenzyme that makes and repairs DNA
Zinc Benefits:
• Zinc is Beneficial for the Skin
• Zinc is Beneficial for the Immune System
• Zinc is Beneficial for the Intestinal Lining
Best Sources of Zinc:
- Seafood
- Seaweed
- Fish
- Liver
- Meat
- Veggies
- Nuts
Additional-resources
- Download My FREE guide: First Signs of a Nutrient Deficiency
Zinc Test:
FAQ
How do I know if my zinc levels are low?
Several signs can indicate low zinc levels:
- Impaired taste and smell
- Slow wound healing
- Hair loss or thinning
- Unexplained weight loss
- Decreased appetite
- Frequent infections due to weakened immune system
- Skin issues like acne or rashes
A simple zinc taste test can also be performed at home. For a definitive diagnosis, consult a healthcare professional for a blood test or hair mineral analysis.
What disease is caused by lack of zinc?
Severe zinc deficiency can lead to various health issues:
- Acrodermatitis enteropathica: A rare inherited condition causing skin inflammation and diarrhea
- Growth retardation in children
- Hypogonadism in males
- Impaired wound healing
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Cognitive impairment
- Night blindness
While not diseases per se, these conditions are directly linked to zinc deficiency and can significantly impact overall health and quality of life.
What blocks zinc absorption?
Several factors can interfere with zinc absorption:
- Phytates found in whole grains, legumes, and nuts
- High calcium intake
- Iron supplements
- Certain medications (e.g., some antibiotics and diuretics)
- Alcohol consumption
- Chronic diseases affecting the digestive system (e.g., Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis)
- High consumption of processed foods and refined sugars
To maximize zinc absorption, consider consuming zinc-rich foods separately from these potential inhibitors and focus on a balanced, whole-food diet.
How can I increase my zinc levels quickly?
To boost zinc levels rapidly:
- Consume zinc-rich foods like oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, and fortified cereals
- Consider a high-quality zinc supplement (consult a healthcare provider for appropriate dosage)
- Pair zinc-rich foods with protein for better absorption
- Reduce consumption of foods high in phytates
- Address any underlying digestive issues
- Manage stress levels, as chronic stress can deplete zinc
- Ensure adequate vitamin A and B6 intake, as they aid zinc absorption
Remember, it’s essential to maintain a balance, as excessive zinc can lead to adverse effects.
Signs of zinc deficiency in females
Zinc deficiency in females may manifest as:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Fertility issues
- Hair loss or thinning
- Brittle nails
- Skin problems (e.g., acne, eczema)
- Impaired taste and smell
- Weakened immune system
- Mood changes and irritability
Women should be particularly mindful of zinc intake during pregnancy and lactation, as requirements increase during these periods.
Zinc deficiency symptoms
Common zinc deficiency symptoms include:
- Loss of appetite
- Impaired immune function
- Slow wound healing
- Hair loss
- Diarrhea
- Eye and skin lesions
- Delayed sexual maturation
- Impaired cognitive function
- Taste abnormalities
- Growth retardation in children
These symptoms can vary in severity and may overlap with other conditions, so professional medical advice is recommended for accurate diagnosis.
Zinc deficiency neurological symptoms
Neurological symptoms of zinc deficiency may include:
- Cognitive impairment and difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems
- Mood disorders (e.g., depression, anxiety)
- Altered behavior or irritability
- Decreased sense of taste and smell
- Peripheral neuropathy (tingling or numbness in extremities)
- Ataxia (lack of muscle control or coordination)
Long-term zinc deficiency can potentially contribute to neurodegenerative disorders, highlighting the importance of maintaining adequate zinc levels for neurological health.
Zinc deficiency symptoms skin
Skin-related symptoms of zinc deficiency can include:
- Acne or pimples
- Eczema or dermatitis
- Slow wound healing
- Stretch marks
- Dry, rough skin
- Rashes or skin lesions
- Brittle or slow-growing nails
- Hair loss or thinning
Zinc plays a crucial role in skin health and repair, so addressing deficiency can often lead to noticeable improvements in skin condition.
Symptoms of zinc deficiency in males
Males with zinc deficiency may experience:
- Hypogonadism (reduced testosterone production)
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased sperm count and quality
- Prostate problems
- Loss of body hair
- Delayed sexual maturation in adolescents
- Muscle wasting
- Increased risk of male-pattern baldness
Adequate zinc intake is particularly important for male reproductive health and hormonal balance.
Zinc deficiency face
Facial signs of zinc deficiency can include:
- Acne or pimples, particularly around the mouth and chin
- Dry, flaky skin
- Pale complexion
- Dark circles under the eyes
- Premature wrinkling
- Angular cheilitis (cracks at the corners of the mouth)
- Hair loss, including eyebrows and eyelashes
These facial symptoms often improve with proper zinc supplementation and dietary changes.
Zinc deficiency diseases
While zinc deficiency itself is not a disease, it can contribute to or exacerbate various health conditions:
- Immune system disorders
- Growth retardation
- Cognitive impairment
- Infertility
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Chronic liver disease
- Sickle cell disease
- Wilson’s disease (a genetic disorder affecting copper metabolism)
Maintaining adequate zinc levels is crucial for preventing and managing these conditions.
Causes of zinc deficiency
Zinc deficiency can result from various factors:
- Inadequate dietary intake, especially in vegetarian or vegan diets
- Malabsorption due to digestive disorders (e.g., Crohn’s disease, celiac disease)
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes, liver disease, sickle cell disease)
- Certain medications (e.g., diuretics, acid-reducing drugs)
- Increased physiological demands (e.g., pregnancy, lactation, rapid growth)
- Excessive sweating in athletes or those living in hot climates
- Soil zinc depletion affecting crop nutrient content
Identifying and addressing these underlying causes is essential for effectively managing zinc deficiency.