Table of Contents
Brief The Article:
1. Zinc and Mental Health:
- Zinc acts as a natural antidepressant
- Zinc deficiency is common in patients with major depressive disorders
- Zinc supplementation may help with depression and mood disorders
2. Zinc’s Role in Brain Function:
- High concentration in neurons around the amygdala and hippocampus
- Influences stress responses and memory formation
- Contributes to spatial memory and overall brain health
3. Zinc and Neurotransmitters:
- Binds to dopamine, which is associated with pleasure
- Involved in the production of proteins, including neurotransmitters
- Deficiency can lead to nervous system degeneration
4. Zinc Deficiency and Skin Disorders:
- Can cause acne, eczema, dermatitis, and rosacea
- May lead to dry skin due to reduced sebum production
- Associated with skin ulcers, bed sores, and diaper rash
- Can cause hyperpigmentation, alopecia, cracked skin, and nail changes
5. Zinc as an Anti-inflammatory:
- Used in various skin creams for healing and treatment
- Acts as a natural anti-inflammatory agent
- Skin is the third most zinc-abundant tissue in the body
6. Future Topics Mentioned:
- Zinc’s influence on blood sugar and insulin
- Impact on the immune system
- Effects on prostate health and testosterone
Hey guys, we’re back! And this time, we’re diving deep into how Zinc Deficiency Affects Skin. You might be surprised to learn just how crucial this mighty mineral is for keeping your complexion clear and healthy.
In this article, we’ll explore the surprising ways that Zinc Deficiency Affects Skin, from acne to eczema and beyond. Plus, we’ll uncover how ensuring you have enough zinc can help you achieve the radiant, healthy skin you’ve always dreamed of. So, if you’re ready to unlock the secrets to vibrant skin, let’s get started and discover how Zinc Deficiency Affects Skin!
So let’s dive into the details…
Zinc Benefits for Mental Health

hey guys we’re back i’m talking about zinc this is part two if you have not uh seen part one i put a link down below you can check that out first first thing i wanna touch on is depression
zinc is a natural antidepressant okay in patients that have major depressive disorders they’re usually always deficient in zinc so if you have depression it’s such a simple remedy take some zinc
it might just help you but generally if you’re deficient in zinc you get degeneration of your nerves of your nervous system. And remember, Zinc Deficiency Affects Skin too, so it’s important to keep that in mind.
Zinc’s Role in Depression and Nervous System Health
- Zinc is a natural antidepressant
- Major depressive disorder patients are often zinc-deficient
- Zinc deficiency can lead to nervous system degeneration
now there’s a lot of concentration of zinc in the neurons around the amygdala and the hippocampus specifically the dentate gyrus
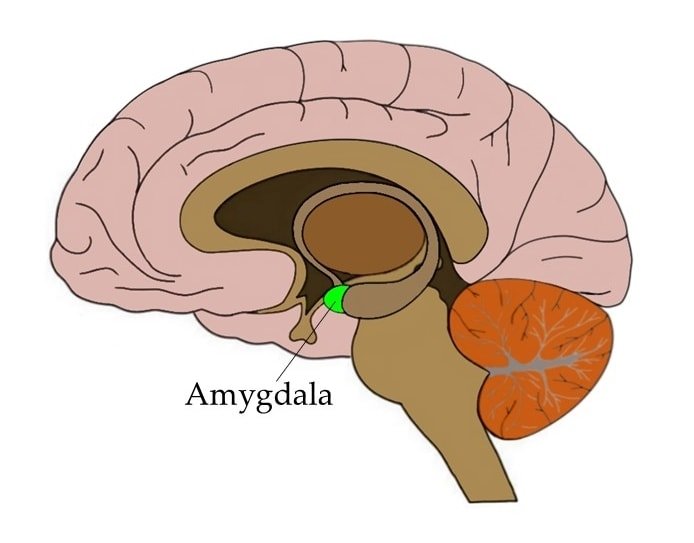
I don’t know how to pronounce him now the amygdala is this part of the brain that’s involved with stress responses it’s kind of you can look at it like the adrenal gland in your brain because it reacts and adapts to stress the hippocampus which they don’t know exactly what it does
but it’s involved in like a relay switch with your memories forming new memories
Zinc’s Importance in Brain Function
- High concentration of zinc in neurons around amygdala and hippocampus
- Amygdala involved in stress responses
- Hippocampus involved in memory formation and spatial memory
and spatial memory like trying to find your way out of some maze it’s kind of like your GPS it helps you locate things in space
the hippocampus in general has a very interesting capacity to regenerate and this is why things that are connected to memory loss focus concentration can be improved with intermittent fasting
so well because intermittent fasting stimulates the regeneration of this part of the brain right here and these structures right here directly influence one’s mood dopamine for example binds to
Zinc and Brain Health
- Hippocampus has capacity to regenerate
- Intermittent fasting can improve memory, focus, and concentration
- Brain structures influenced by zinc affect mood
zinc so dopamine gives you pleasure so what’s the opposite of pleasure depression right also it’s involved in like I said before making proteins and guess what neurotransmitters are they’re proteins
so if you have any problem with depression or any type of mood disorder take zinc it can potentially help you greatly
Zinc’s Impact on Mood and Neurotransmitters
- Zinc binds to dopamine, which gives pleasure
- Zinc is involved in making proteins, including neurotransmitters
- Zinc supplementation can potentially help with depression and mood disorders
Zinc Deficiency Affects Skin

all right now let’s shift to skin disorders It’s important to understand how Zinc Deficiency Affects Skin because it can manifest in many ways.
now you may already know this but there’s so many different skin creams and skin healing creams that involve zinc and if you’re zinc deficient you can get
acne eczema dermatitis many different types of dermatitis rosacea a zinc deficiency can dry out the oil in the skin it’s called the sebum
it can lead to ulcers of the skin both superficially and internally like ulcers of the stomach or ulcers in the mouth or even like bed sores one of the treatments for bed sores is a zinc cream
that you would put on it or even diaper rash for example irritation in the skin you use this zinc so you can look at zinc as a natural anti-inflammatory so a zinc deficiency can also lead to
Skin Conditions Related to Zinc Deficiency
- Acne, eczema, dermatitis, rosacea
- Dry skin due to sebum reduction
- Ulcers (skin, stomach, mouth)
- Bed sores and diaper rash

hyperpigmentation on the skin and alteration in color alopecia is where you have hair loss in different patches this is an autoimmune condition with cracked skin
that’s fissured nail changes and skin is the third most zinc-abundant tissue in the entire body. We’ll explore more about how Zinc Deficiency Affects Skin in the next section.
all right guys stay tuned for part three
when we get into the relationship between zinc influencing your blood sugars and insulin your immune system and the prostate and testosterone hey guys real quick i have a new healthy keto eating plan for you
Additional Skin Issues Related to Zinc Deficiency
- Hyperpigmentation and color alteration
- Alopecia (patchy hair loss)
- Cracked and fissured skin
- Nail changes
Note: Skin is the third most zinc-abundant tissue in the body
Summary
In this part 2 of 3 series topic where Dr. Berg talks about the amazing benefits of zinc and how zinc deficiency affects the skin.
Depression
- Zinc is a natural anti-depressant
Zinc Deficiency Signs of the Skin
- Acne
- Eczema
- Dermatitis
- Rosacea
- Dry out oil in the skin
- Ulcers of the skin
- Increase Inflammation
- Hyperpigmentation
- Alopecia
- Cracked Skin
- Nail Changes
- Diaper Rash
Additional Resources:
FAQ
How does zinc deficiency affect the skin?
Zinc deficiency can have significant impacts on skin health:
- Increased susceptibility to acne, eczema, dermatitis, and rosacea
- Dry skin due to reduced sebum production
- Higher risk of skin ulcers, bed sores, and diaper rash
- Hyperpigmentation and slower wound healing
- Potential hair loss (alopecia) and nail changes
- Cracked or flaking skin
How does zinc heal skin?
Zinc plays a crucial role in skin healing:
- Acts as a natural anti-inflammatory agent
- Promotes collagen synthesis, essential for skin repair
- Supports cell division and growth, accelerating wound healing
- Regulates sebum production, helping with acne and oily skin
- Protects against UV radiation damage
- Used in various skin creams and ointments for its healing properties
How does zinc affect us?
Zinc affects multiple aspects of our health:
- Supports immune function and fights infections
- Plays a role in DNA synthesis and cell division
- Crucial for protein synthesis and enzyme function
- Influences brain function, including memory and mood regulation
- Important for growth and development, especially in children
- Aids in wound healing and maintaining skin health
- Supports sensory functions like taste and smell
What organ does zinc affect?
Zinc affects multiple organs and systems:
- Brain: Influences neurotransmitter function and cognitive processes
- Skin: Third most zinc-abundant tissue in the body
- Immune System: Crucial for immune cell function
- Digestive System: Aids in nutrient absorption and enzyme production
- Reproductive Organs: Important for fertility and hormone production
- Endocrine System: Affects hormone synthesis and regulation
- Bones: Necessary for bone mineralization and growth
Benefits of zinc sexually
Zinc plays a role in sexual health:
- Boosts testosterone production in men
- Supports prostate health and function
- May improve sperm quality and motility
- Helps regulate hormones in both men and women
- Can increase libido and sexual performance
- Supports overall reproductive health
Signs of zinc deficiency in females
Common signs of zinc deficiency in females include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Hair loss or thinning
- Slow wound healing
- Weakened immune system, leading to frequent infections
- Skin issues like acne or eczema
- Loss of appetite or altered taste perception
- Mood changes, including depression or anxiety
- Fertility issues or pregnancy complications
Zinc deficiency symptoms
General symptoms of zinc deficiency include:
- Impaired immune function and increased susceptibility to infections
- Delayed wound healing
- Skin problems (acne, eczema, dry skin)
- Hair loss
- Loss of appetite or altered taste
- Cognitive impairment and mood disorders
- Growth retardation in children
- Diarrhea
- Reduced fertility
- Night blindness or impaired vision
Zinc benefits for women
Zinc offers several benefits for women:
- Supports reproductive health and fertility
- May help regulate menstrual cycles
- Boosts immune system function
- Promotes healthy skin, hair, and nails
- Supports cognitive function and mood regulation
- May help reduce PMS symptoms
- Important for fetal development during pregnancy
- Can aid in postpartum recovery
Is 50mg of zinc too much?
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for zinc is:
- 11 mg per day for adult men
- 8 mg per day for adult women
50mg of zinc daily is above the RDA and the tolerable upper intake level of 40mg/day. While short-term use of higher doses may be prescribed for specific conditions, prolonged intake of 50mg daily can:
- Interfere with copper absorption
- Cause nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and headaches
- Potentially weaken immune function if used long-term
Always consult a healthcare professional before taking high-dose supplements.
Zinc Tablets benefits
Zinc tablets can provide various benefits:
- Support immune system function
- Aid in wound healing
- Help maintain healthy skin
- Support cognitive function and mood regulation
- May reduce the duration and severity of common colds
- Support eye health, potentially reducing age-related vision decline
- Aid in protein synthesis and cell growth
- Support male reproductive health
Always follow recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
Benefits of zinc for men
Zinc offers several specific benefits for men:
- Supports testosterone production
- Promotes prostate health
- May improve sperm quality and motility
- Supports muscle growth and recovery
- Aids in maintaining healthy hair
- Supports cognitive function and mood regulation
- Boosts immune system function
- May help prevent age-related macular degeneration
How much zinc per day for a woman?
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for zinc in women varies:
- Adult women (19+ years): 8 mg per day
- Pregnant women: 11 mg per day
- Breastfeeding women: 12 mg per day
Factors that may increase zinc needs:
- Vegetarian or vegan diets
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., Crohn’s disease, liver disease)
- Alcohol use
Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice, especially if considering supplements.




