Table of Contents
normal vitamin D levels explained
Understanding normal vitamin D levels is crucial for maintaining optimal health. This article explores the standard ranges for vitamin D, its sources, and the potential risks of deficiency and toxicity. Learn how to manage and monitor your vitamin D levels effectively.
We all know how important vitamin d is , but it’s also incredibly confusing to know amounts that you need . And does the amount of vitamin d in your blood really tell you what’s going on in the cells ?
Now when you get your blood test done with vitamin d , some references give you this , normal range between 20 to 40 nanograms per milliliter .
Other references are between 30 and 50 nanograms per milliliter .
And , of course , if you’re in a different part of the world , there’s different values .
So , for example , if you have 50 nanograms per milliliter , that would be a 125 nanomoles per liter .
So as you can see , it’s very , very confusing .
And especially if you take vitamin d , which is in a different measurement altogether , which is in international units , Even that’s very confusing because when we talk about vitamin d 3 , 1 international unit equals 0.025 micrograms .

And when you talk about other things like beta carotene or retinol , it’s in a completely different system .
It doesn’t equal what I just mentioned .
So it’s very confusing .
Even the RDAs for vitamin d , for someone that’s under 70 years old , is 600 IUs , okay , which is 15 micrograms .
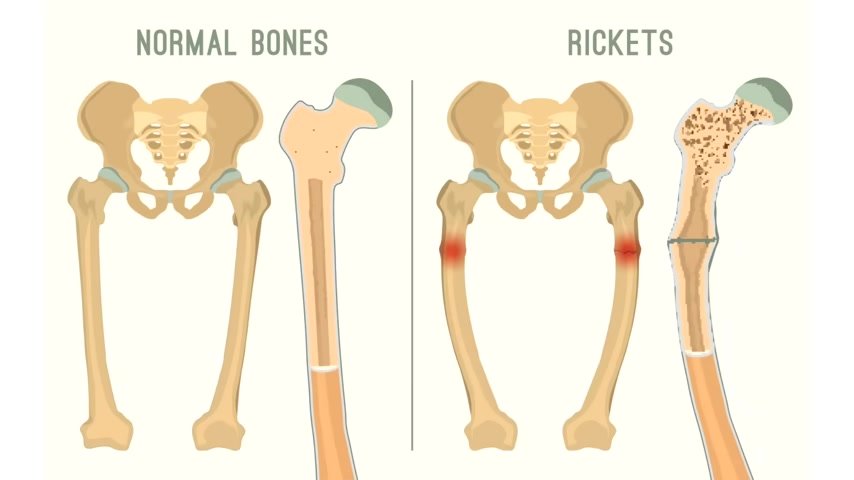
And the studies that validate that amount , which is extremely low , were done years ago designed to prevent rickets .
But that was way before all this new information on how vitamin d supports the immune system and so many other biological systems .
Understanding the vitamin D receptor
So checking your , vitamin d levels in the blood is is all fine , and that’s that’s great .
But the most important thing about vitamin d is , does it reach the cell ?
And it reaches the cell through the vitamin d receptor .
And , unfortunately , you cannot use the blood levels of vitamin d to determine what’s going on in your cell simply because there’s so many problems with the vitamin d receptor .
Certain viruses and other pathogens have a mechanism , a survival mechanism of blocking your vitamin d receptor for their survival because they know if that vitamin d goes into that cell , they’re toast .
Also , certain cancers have a survival mechanism of downgrading the vitamin d receptor to make sure you don’t get enough because of this huge association between vitamin d and the reduction of cancer risk .

I mean , if you think about even in a benign tumor , you get it like a 93% absorption with that vitamin d receptor .
But in a malignant cancer , the vitamin d receptor now goes from 93 down to 56 absorption .
So you can see that cancer cell tends to block the absorption of vitamin d .
And about 30% of the population has a genetic problem with the vitamin d receptor , including myself .
So normal amounts of vitamin d do not , make the changes that I need .
So what do we do ?
How do we solve this problem ?
Well , number 1 , might be a good idea to get a genetic test to measure your vitamin d receptor .
But there’s some other simple things you can do .
Does vitamin d receptor diseases and problems run-in your family , or do you have a problem with those ?
And I’m gonna list them right now .
But there are so many diseases and health related conditions that are directly related to a problem with the vitamin d receptor .
So let me just go down the list right now .
Autoimmune diseases , and this includes MS , lupus , rheumatoid arthritis , psoriasis , Hashimoto’s , ankylosing spondylitis .
The next category , certain types of cancer , especially breast cancer and colon cancer .
You just have to realize how important vitamin d is for so many things , including every aspect of your immune system that bites off cancer .
Normally , the immune cells are supposed to kill cancer , if they have enough vitamin d , but not if they don’t have enough vitamin d .
Certain cardiovascular diseases are related to a problem with the vitamin d receptor .
Certain cognitive diseases , including Alzheimer’s , Parkinson’s are associated with a problem with the vitamin d receptor .
Then we have diabetes , type 1 and type 2 .
And type 1 is an autoimmune disease , so that would definitely fit into that vitamin d problem .
Next one is metabolic syndrome , which includes high blood pressure , lipid problems , high blood glucose or diabetes .
Next one is TB .
Tuberculosis , which is a huge problem with the vitamin d receptor .
In fact , years ago , some of the earlier treatments for TB was just getting out in the sun , and that would greatly help TB because of the production of vitamin d .
And if you ever have the choice between getting your vitamin d from a pill form versus the sun , you’d be better to get it from the sun .

That would be the ideal situation if you can get vitamin d from the sun .
So we have TB .
We also have , certain viruses , parasites , some bacteria .
Lyme disease , definitely associated with a vitamin d receptor issue .
Hair loss , Crohn’s , other types of GI inflammation issues .
Because what you have to remember is that vitamin d is probably one of the best natural anti inflammatories .
And then we get respiratory infections , huge association with a vitamin d receptor , probably because there’s certain viruses involved that tend to hijack the vitamin d receptor .
And then we get asthma .
If a child has asthma and you get them to be outside in the fresh air and the sun , boy , their rate of getting asthma just goes way down .
Food allergies .
The more food allergies you have , the more problems you have with the vitamin d receptor .
And then we get a really common thing , low back pain , definitely associated with the vitamin d .
Vitiligo , a situation where you have , a lack of pigment in certain places in your body .
Then you have osteoporosis , COPD , which is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease .
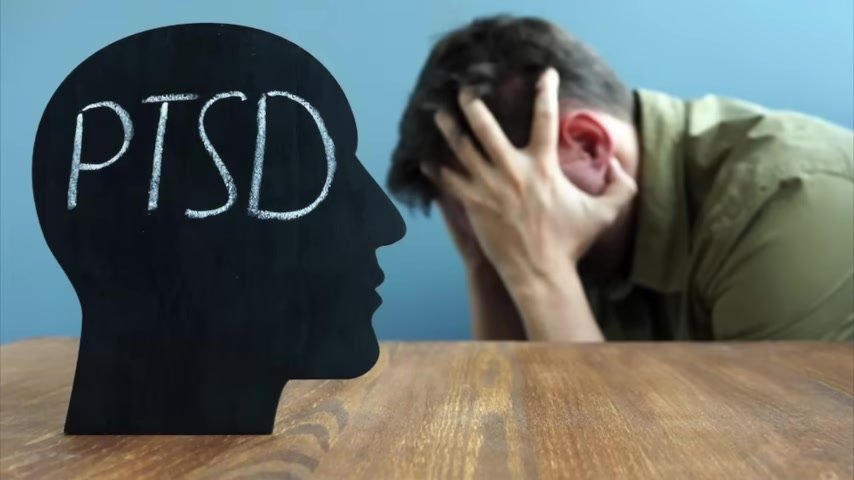

And then even PTSD is associated with low vitamin D , probably because vitamin d greatly helps depression .
How to boost low vitamin D
So beyond checking your blood , which is good to do , but if you still have problems , you’re probably gonna benefit from taking more vitamin D .
So number 1 , take more vitamin d .
It’s that simple .
And you might need 20 , 30 , 40 , 50 1000 IUs .
If you start seeing changes , then we know regardless of how much vitamin d you have in your blood that you were deficient in the cell because you had a vitamin d receptor issue .
Number 2 , take it inconsistently .
Like , instead of taking it on a regular basis , okay , you might wanna take it once every 3 days or once every 4 days and take a good amount .
Apparently , that’s a good strategy for certain people that have a problem with the vitamin d receptor .
Even though I personally have a problem with vitamin d , I do take it consistently each day just because it’s easy to remember .
But if I had an autoimmune disease or some of these other problems , I might take it , sporadically .

You can take magnesium .
That will help the vitamin d receptor .
You can take zinc .
You can take bile salts .
Now bile salts are interesting because they act as a vitamin d receptor analog .
What does that mean ?
It means that you can trigger the gene for vitamin d without necessarily taking vitamin d .
It’s pretty wild .
You can take it in the form of Tatka as well , or just bile salts .
Omega 3 has been known to increase the vitamin d receptor .
Vitamin k 2 also helps .
And then you have various , plant chemicals that are also really good to increase the reception of the vitamin d receptor , like resveratrol , curcumin , quercetin , and sulforaphane .
All of those can greatly help .
And the last thing that can help vitamin d is butyrate .
Now what’s butyrate ?
That is a short chain fatty acid that’s produced by your own microbes .
And you can increase the production of that if you consume vegetables , because the vegetables provide fiber for the microbes .
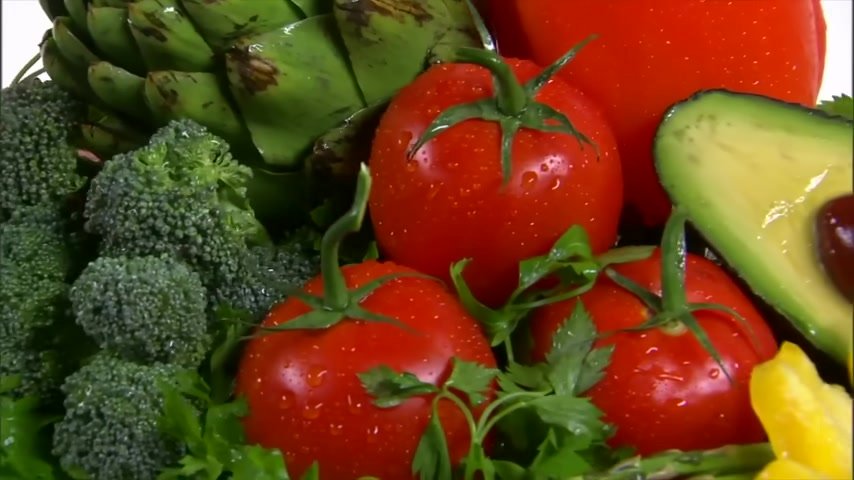

They eat that .
They convert it to butyrate , and then that can help your absorption of vitamin d .
It can also help you with insulin resistance , and butyrate is a form of a ketone .

So , of course , I would recommend also being on the ketogenic diet , which will help insulin resistance .
DATA:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6259298
Key Points:
Many health conditions are directly related to a problem with the vitamin D receptor, including:
• Autoimmune diseases
• Breast cancer and colon cancer
• Certain cardiovascular diseases
• Certain cognitive diseases
• Diabetes (type 1 and type 2)
• Metabolic syndrome
• High blood pressure
• Tuberculosis and certain infections
• Lyme disease
• Hair loss
• Crohn’s disease
• Respiratory infections
• Asthma and food allergies
• Low back pain
• Vitiligo
• Osteoporosis
• COPD
• PTSD
How to increase vitamin D:
- Take more vitamin D
- Take your vitamin D supplements inconsistently
- Take magnesium
- Take zinc
- Take bile salts
- Consume omega-3 fatty acids
- Consume vitamin K2
- Take resveratrol, curcumin, quercetin, and sulforaphane
- Consume butyrate (vegetables)




