Table of Contents
Explore the crucial link between potassium-insulin function. Learn how potassium impacts insulin resistance, blood sugar levels, and overall health, especially for diabetics
Insulin is a hormone that plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels and storing glucose as glycogen. However, did you know that potassium is essential for insulin function and overall metabolic health?
In this article, we delve into the critical connection between potassium and insulin. Potassium helps improve insulin resistance, making it particularly beneficial for diabetics. A high glucose or carbohydrate diet can deplete potassium from the cells, leading to symptoms like increased pulse rate, difficulty sleeping, and high blood pressure.
Discover how adequate potassium intake can support insulin function, regulate blood sugar levels, and improve overall health. Learn about the best dietary sources of potassium and how to ensure you get enough of this essential mineral, especially if you are managing diabetes.
Today I wanna talk about the relationship between potassium and insulin .
It’s very interesting especially if you are a diabetic or have insulin resistance .
So insulin is a hormone that causes you to store fat .
How insulin works

In the presence of insulin , it’s almost impossible to burn fat and lose weight because insulin prevents the fat burning .
So it’s all about storing , sugar as fat and it’s preventing the oxidation or breakdown of fat .
Insulin also stores glucose .
So let’s say for example you ate some sugar or some refined carbs , now the the body is going to store that as stored sugar .
Glycogen
Insulin turns glucose into glycogen .
So this is what glycogen looks like .
It’s a string of glucose molecules held together as stored sugar , and you also have potassium involved as well .
So potassium is necessary in the storage of glycogen .
potassium-Insulin
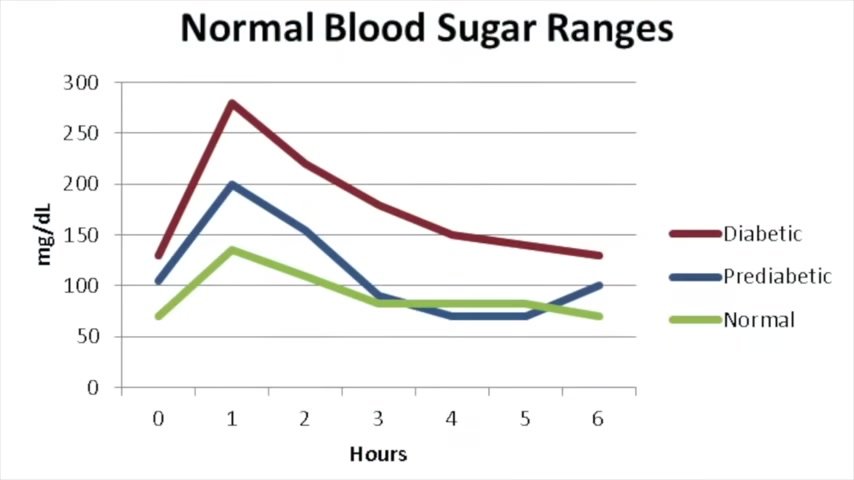
So the main purpose of insulin is to lower your blood sugar , and it does that through taking the sugar and putting into storage as glycogen or as fat .
And if you’re diabetic and you take medication to lower your blood sugar , the question is , so where is it going ?
It’s being hidden as fat .
It’s not evaporating .
So basically these medications are taking out of the blood , and putting it somewhere else .
Now insulin also helps put potassium in your cells .
So that’s one of the purposes .
When you consume a high glucose diet or a high carb diet , you deplete potassium from the inside of the cell .
So you lose potassium .
So if you consume a lot of carbohydrates at one time , you’re gonna show potassium deficiency symptoms like your pulse rate will start going up .

You’ll have a hard time sleeping .
Your blood pressure might go up .
You may feel , palpitations in your heart or heart arrhythmia type symptoms .
Potassium and insulin resistance
Taking potassium makes insulin less resistive as well .
So it’s really good to improve insulin resistance .
And if you’re diabetic , you have insulin resistance .
And this is why all diabetics should be making sure they get enough potassium and more to help their blood sugars and improve , the normalization of insulin .
Potassium deficiency

If you’re deficient in potassium , that’s gonna impair glucose and even increase the risk for insulin resistance just by having a deficiency of potassium .
And then you’re being put on a medication like a diuretic which then can deplete potassium and cause more high blood pressure .
And also if you have insulin resistance and you’re diabetic , you take metformin and one of the problems with metformin , it depletes potassium .
key Points:
- Insulin is a hormone that causes you to store fat. In the presence of insulin, it’s almost impossible to burn fat and lose weight because insulin prevents fat burning. With insulin, you store sugar as fat, and it prevents the break down of fat. Insulin also stores glucose and turns glucose into glycogen.
- Glycogen is a string of glucose molecules held together as stored sugar. Potassium is also involved. Potassium is necessary in the storage of glycogen.
- The main purpose of insulin is to lower your blood sugar. It does that by taking the sugar and putting it in storage as glycogen or as fat.
- Insulin also helps put potassium in your cells. When you consume a high-carb diet, you deplete potassium from the inside of the cell—you lose potassium.
- Taking potassium makes insulin less resistive. Potassium may be very beneficial if you have insulin resistance. If you’re a diabetic, you have insulin resistance.
- If you’re deficient in potassium, that situation will impair glucose and even increase the risk of insulin resistance.
- It is very important to get enough potassium—especially if you have a blood sugar issue.
DATA
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11255-015-1001-5
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21734082
FAQ:
How is insulin related to potassium?
Insulin plays a crucial role in regulating potassium levels in the blood. When insulin is released, it helps transport glucose into cells, and simultaneously, it promotes the uptake of potassium into cells. This process helps lower blood potassium levels, maintaining a proper balance.
What is the relationship between potassium and insulin in DKA?
In Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), insulin deficiency leads to high blood sugar and ketone production. As a result, potassium shifts out of cells into the bloodstream, causing hyperkalemia (high potassium levels). Treatment with insulin helps normalize blood sugar and potassium levels, but it can also lead to hypokalemia (low potassium levels) if not monitored closely.
What is the relationship between hyperglycemia and hyperkalemia?
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) can lead to hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) because high glucose levels cause water and potassium to move out of cells into the bloodstream. This shift increases serum potassium levels. Effective blood sugar management is essential to prevent hyperkalemia.
Do potassium and glucose have an inverse relationship?
Yes, potassium and glucose often have an inverse relationship in the body. High glucose levels can cause potassium to move out of cells into the bloodstream, raising serum potassium levels. Conversely, insulin administration lowers blood glucose and promotes potassium uptake into cells, potentially decreasing serum potassium levels.
Potassium and blood sugar relationship
Potassium and blood sugar levels are closely linked. Insulin helps transport glucose into cells and also promotes the uptake of potassium into cells. Therefore, high blood sugar can cause potassium to shift out of cells, while insulin therapy can lower both blood sugar and potassium levels.
Does insulin cause hypokalemia or hyperkalemia?
Insulin primarily causes hypokalemia (low potassium levels). It promotes the uptake of potassium into cells, which lowers the potassium levels in the bloodstream. However, improper insulin administration without monitoring can lead to dangerously low potassium levels.
How does insulin cause hypokalemia?
Insulin causes hypokalemia by promoting the uptake of potassium into cells. When insulin is administered, it facilitates the entry of glucose into cells, and potassium follows suit. This process decreases the potassium levels in the bloodstream, potentially leading to hypokalemia.
Potassium and diabetes type 2
People with type 2 diabetes often experience fluctuations in potassium levels due to insulin resistance and medication use. Proper management of blood sugar levels is crucial to maintain balanced potassium levels, as both hyperglycemia and insulin therapy can affect potassium distribution in the body.
High potassium and insulin
High potassium levels (hyperkalemia) can occur in people with diabetes due to insulin deficiency or resistance. Insulin therapy is often used to treat hyperkalemia because it helps transport potassium back into cells, thus lowering serum potassium levels.
Insulin and potassium mechanism
The mechanism of insulin and potassium involves insulin facilitating the transport of glucose and potassium into cells. When insulin binds to its receptors, it activates pathways that increase the uptake of glucose and potassium, helping to maintain balanced blood sugar and potassium levels.
Does DKA cause hypokalemia or hyperkalemia?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) initially causes hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) due to insulin deficiency and acidosis. However, treatment with insulin can shift potassium back into cells, potentially leading to hypokalemia (low potassium levels) if not monitored and corrected appropriately.
Potassium and diabetes type 1
In type 1 diabetes, potassium levels can be affected by insulin therapy and blood sugar control. Insulin helps regulate potassium by promoting its uptake into cells, but poor blood sugar management can lead to imbalances. Monitoring and managing potassium levels is essential for individuals with type 1 diabetes, especially during episodes of DKA.




