Table of Contents
You know, zinc is a crucial mineral for countless bodily functions. But did you know that even if you’re eating zinc-rich foods, you might not be absorbing zinc properly? Let’s delve into 8 surprising factors that could be hindering your ability to absorb zinc and discover how to optimize your intake for optimal health.
Brief The Article:
Why is zinc important?
Zinc is essential for metabolism, immune function, protein metabolism, enzyme function, and neuron function. It plays a vital role in many chemical reactions in the body.
8 Reasons why you might not be absorbing zinc?
1. Low Stomach Acid:
- Insufficient stomach acid can impair the absorption of zinc.
- Signs of low stomach acid include heartburn, antacid use, GERD, and indigestion.
- Age-related decline in stomach acid can also affect zinc absorption.
2. Phytates in Diet:
- Phytates (phytic acid) found in whole grains, especially brown rice, are a major inhibitor of zinc absorption.
- High consumption of phytate-rich foods is a significant contributor to zinc deficiency worldwide.
3. Cadmium Exposure:
- Cadmium, a heavy metal found in tobacco and seafood, can interfere with zinc absorption.
- Smokers may require higher zinc intake to compensate for potential cadmium exposure.
4. Low Protein Intake:
- Zinc absorption is enhanced by amino acids, so low protein diets can hinder the process.
- Vegan diets, if not properly planned, can lead to zinc deficiency due to low protein and high phytate intake.
- Inadequate stomach acid can also impair protein digestion and indirectly affect zinc absorption.
- Damage to the small intestine can further hinder protein and zinc absorption.
5. Digestive Issues:
- Digestive problems like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and Crohn’s disease can significantly impair zinc absorption.
6. High Sugar Intake:
- High sugar intake, diabetes, insulin resistance, and high carbohydrate consumption can deplete zinc levels and hinder zinc absorption.
7. Bariatric Surgery:
- Bariatric surgery can lead to zinc deficiency due to the bypass of portions of the small intestine and reduced stomach acid production.
- Individuals who have undergone bariatric surgery should consider supplementing with trace minerals, including zinc.
8. High Iron or Calcium Intake:
- High levels of iron or calcium can interfere with zinc absorption.
- Excessive iron intake can be detrimental to health and can also deplete zinc levels.
Good Sources of Zinc:
- Oysters, meats (especially liver), nuts, and seafood are good sources of zinc.
- Note that oysters also contain heavy metals, but they are rich in selenium, which can help offset the toxic effects.
Key Takeaway:
Understanding these factors that can hinder zinc absorption is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Addressing these issues and ensuring adequate zinc intake through diet or supplementation can significantly impact various aspects of well-being.
So let’s dive into the details…
Reasons Why You May Not Be Absorbing Zinc

So I wanted to touch on zinc and the eight factors that determine if you can absorb zinc or not because on one hand let’s say for example you have enough in your diet but what about if you cannot absorb zinc?
Zinc is one of the most important trace minerals and nutrients that you could have. It’s involved in so many different chemical reactions with your metabolism, with your immune system and your protein metabolism, enzymes, neuron function, and the list goes on and on and on.,
- Zinc is a crucial trace mineral involved in numerous bodily functions, including metabolism, immune function, protein metabolism, enzyme activity, and neuron function.
- Zinc deficiency can lead to various health problems.
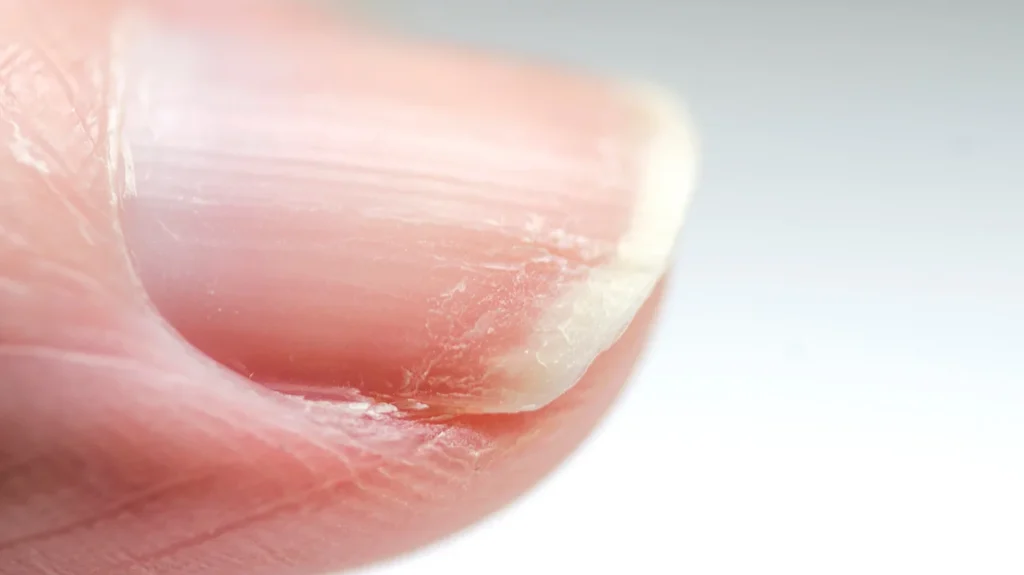
So if you’re deficient in zinc you’ll have problems with your nails, hair loss, skin problems, GI problems like diarrhea, a testosterone deficiency, problem with your immune system.
- Symptoms of zinc deficiency include nail problems, hair loss, skin issues, gastrointestinal problems, testosterone deficiency, and weakened immunity.
Low Stomach Acid and Absorb Zinc
1-Low Stomach Acid and Zinc Absorption

low stomach acids. Okay, if you don’t have enough stomach acid, you will not be able to absorb zinc.
- Low stomach acid hinders zinc absorption.
Now how do you know if you don’t have enough stomach acid? Well, if you have heartburn, if you’re on anti-acids, if you have GERD, sometimes if you have indigestion, chances are you don’t have enough acid in the top of the valve on your stomach.
- Signs of low stomach acid include heartburn, antacid use, GERD, and indigestion.
Doesn’t close properly so the acid just kind of goes right through. As you age, you lose stomach acid and you also lose the ability to absorb minerals. So this would be number one.
- Age-related decline in stomach acid can impair mineral absorption, including zinc.
2-Phytates and Zinc Deficiency

you’re consuming foods with phytate. Okay, or phytic acid. This is a compound especially in whole grains and definitely in brown rice. And this is probably one of the most common reasons why people have such a zinc deficiency.
In fact, two billion people on this planet have a zinc deficiency, and there’s a lot of people consuming grains
- Phytates (phytic acid) found in whole grains, especially brown rice, can significantly inhibit zinc absorption.
- Phytates are a major contributor to zinc deficiency globally.
and brown rice loaded with phytates which can create a zinc deficiency.
- High consumption of phytate-rich foods can lead to zinc deficiency.
3-Cadmium and Absorb Zinc

cadmium. this is a heavy metal. The tobacco plant, for example, will absorb cadmium from the soil, and when you smoke, goes right into your lungs. Also, seafood has cadmium, mercury, and heavy metals. I’m gonna do a separate topic just on this though. So if you’re a smoker, okay, you might want to take a little more zinc.
- Cadmium, a heavy metal found in tobacco and seafood, can interfere with zinc absorption.
- Smokers may require higher zinc intake.
4-Low Protein Diets and Zinc Absorption

low protein diets. Zinc absorption is enhanced with amino acids. If you’re not having enough protein, you’re
- Low protein diets can impair zinc absorption as amino acids enhance the process.
let’s say for example you start a vegan diet and you’re not doing it correctly, you don’t have enough complete protein to diet and also you’re doing whole grains, brown rice, getting loads of phytate, you’re gonna be low in zinc.
- Vegan diets, if not properly planned, can lead to zinc deficiency due to low protein intake and high phytate consumption.
And a couple more points about low protein. If you don’t have enough stomach acid, that could be the reason why you’re not breaking down the protein and absorbing the protein and small intestine. If you have damage within the small intestine itself, you’ll have a hard time absorbing
- Low stomach acid can hinder protein breakdown and absorption, indirectly affecting zinc absorption.
- Damage to the small intestine can also impair protein and zinc absorption.
protein because the small intestine actually releases enzymes to help break down this protein. It’s originally broken down by the stomach from hydrochloric acid into smaller cold peptide chains and but then the small intestine releases its enzymes to take it down to the basic amino acid building blocks so they can be absorbed and then utilized by the body.
- The small intestine plays a crucial role in protein digestion and absorption, which is essential for zinc absorption.
5-Digestive Issues and Zinc Absorption

you have a digestive issue, whether it’s inflammation in the colon as inflammatory bowel syndrome or Crohn’s, which is another inflammatory gut
- Digestive issues like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and Crohn’s disease can impair zinc absorption.
problem, or celiac, which is an autoimmune problem with the gut. If you have a problem with the gut, you’re gonna have a hard time absorbing zinc.
- Gut problems can significantly hinder zinc absorption.
6-High Sugar Intake and Zinc Deficiency

High sugar. If you’re a pre-diabetic or a diabetic or you have insulin resistance or you’re just consuming a lot of carbohydrates, those carbohydrates can deplete your zinc. If your insulin resistant, you’re gonna have a hard time absorbing zinc.
- High sugar intake, diabetes, insulin resistance, and high carbohydrate consumption can deplete zinc levels and impair zinc absorption.
7-Bariatric Surgery and Zinc Deficiency
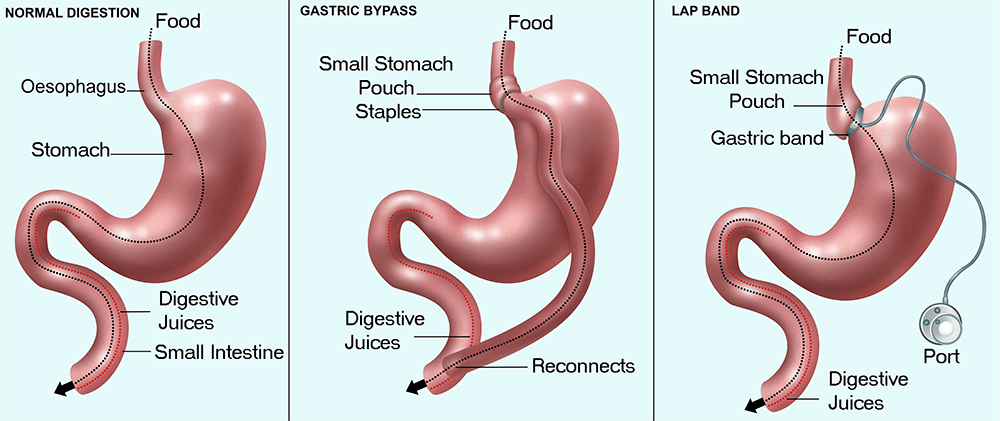
Bariatric Surgery. Why would that prevent your absorption of zinc? Well, because they’re bypassing some of your small intestine
- Bariatric surgery can lead to zinc deficiency due to the bypass of portions of the small intestine and reduced stomach acid production.
and your stomach. So you’ve decreased the surface area of absorption as well as decrease the ability to make stomach acid, and you could potentially end up with a zinc deficiency.
This is one reason why people that had a gastric bypass should be taking trace minerals. Very important.
- Individuals who have undergone bariatric surgery should consider supplementing with trace minerals, including zinc.
8-High Iron or Calcium Intake and Zinc Absorption

high amounts of iron or calcium. Both of these minerals can block your absorption of zinc. There’s quite a few people that have too much iron from a genetic problem, and even if they don’t, it’s very
- High levels of iron or calcium can interfere with zinc absorption.
difficult to iron especially men because men don’t menstruate like women. Of course, women after menopause could have higher amounts of iron.
But think about iron is it’s very dangerous at high levels and it’s very dangerous at low levels. You just need certain amounts. But the bottom line is the body has a hard time getting rid of iron.
So if someone’s taking an iron from a supplement, for example, especially if it’s the wrong type, it’s not a food-based supplement, they can build up a lot of iron, create a lot of
- Excessive iron intake can be detrimental to health and can also deplete zinc levels.
problems and also deplete the zinc. Same thing goes with calcium. If you have too much calcium, you’re gonna have a problem with the absorption of zinc.
These are Good Sources of Zinc
Food Sources of Zinc

Now where do you get zinc from? Oysters have the most, but realize that ores also have some heavy metals. However, oysters also have selenium, which can help to offset that toxic effect.
I’m gonna do a separate topic on seafood very shortly so you can check out that topic. Also, meats, liver will have zinc, nuts, and seafood has it as well.
- Good sources of zinc include oysters (which also contain heavy metals but are rich in selenium), meats (especially liver), nuts, and seafood.
Summary
- Zinc is one of the most important nutrients and trace minerals you can have. It’s involved in many processes for your metabolism, immune system, protein metabolism, enzymes, neuron function, and more.
- If you have problems with zinc, you’ll have nail issues, hair loss, skin and GI problems like diarrhea, low testosterone, and problems with your immune system.
The 8 reasons you may not be absorbing zinc are:
- Low stomach acid. You’ll know if you have it if you have heartburn, are on antacids, or have GERD, for example.
- You’re consuming foods with phytate (phytic acid), a compound in whole grains and brown rice.
- Cadmium, a heavy metal. Tobacco contains this, as does seafood, which also has mercury and other heavy metals. If you’re a smoker, take zinc.
- Low protein diets. Zinc is enhanced by amino acids that are the building blocks of protein. If you’re on a vegan diet but not doing it correctly, you may be too low in protein. Because you’re also consuming grains and rice, you’re almost certainly going to be low in zinc, especially if you also have damage to your small intestine.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s, or celiac disease
- High blood sugar, if you’re prediabetic or diabetic, or have insulin resistance, or are consuming a lot of carbohydrates
- Bariatric surgery, which decreases the available GI surface area for nutrient absorption as well as your ability to make stomach acid. If you’ve had a gastric bypass, you should be taking trace minerals.
- High amounts of iron or calcium; for iron, possibly from a genetic condition, or if you’re a man you could have difficulty ridding your body of iron since you don’t menstruate.
These are good sources of zinc: oysters, meat, nuts, and seafood. Be sure to consume these so you can boost your zinc intake and start to correct the 8 reasons why you may not be absorbing zinc.
Additional-resources
FAQ
What factors affect the absorption of zinc?
Several factors can influence zinc absorption:
- Dietary composition: High phytate content in foods can inhibit zinc absorption
- Stomach acid levels: Low stomach acid can reduce zinc absorption
- Protein intake: Adequate protein enhances zinc absorption
- Presence of other minerals: High levels of iron or calcium can interfere with zinc absorption
- Digestive health: Conditions like inflammatory bowel disease can impact absorption
- Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can reduce zinc absorption
Understanding these factors can help optimize zinc intake and absorption for better health outcomes.
What causes zinc not to be absorbed?
Zinc absorption can be hindered by various factors:
- Phytates in whole grains, legumes, and nuts
- Low stomach acid or use of antacids
- Certain medications like diuretics or ACE inhibitors
- Digestive disorders like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease
- High intake of competing minerals (iron, calcium)
- Malabsorption syndromes
- Chronic diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract
Addressing these factors can improve zinc absorption and prevent deficiency.
What blocks absorption of zinc?
Several substances and conditions can block zinc absorption:
- Phytic acid (found in whole grains, legumes, and nuts)
- Excessive calcium or iron intake
- Cadmium exposure (from pollution or cigarette smoke)
- Certain medications (e.g., some antibiotics, diuretics)
- Alcohol consumption
- High fiber diets (if not balanced properly)
- Some forms of processed foods
Being aware of these blockers can help in planning a diet that maximizes zinc absorption.
How to make sure zinc is absorbed?
To enhance zinc absorption:
- Consume zinc with protein-rich foods
- Soak or sprout grains and legumes to reduce phytate content
- Take zinc supplements on an empty stomach or at least 2 hours apart from iron or calcium supplements
- Consume vitamin A and B6, which aid in zinc absorption
- Consider zinc picolinate or zinc methionine, which are more easily absorbed forms
- Maintain a healthy digestive system
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption
Implementing these strategies can significantly improve zinc absorption and utilization in the body.
Benefits of zinc sexually
Zinc plays a crucial role in sexual health:
- Boosts testosterone production in men
- Improves sperm quality and motility
- Enhances libido in both men and women
- Supports prostate health
- May help with erectile function
- Aids in the regulation of hormones
- Supports overall reproductive health
Adequate zinc levels are essential for maintaining optimal sexual and reproductive function in both genders.
Is 50mg of zinc too much?
50mg of zinc daily is above the recommended upper limit for most adults:
- The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for zinc is 11mg for adult men and 8mg for adult women
- The upper limit is set at 40mg per day for adults
- Consuming 50mg regularly may lead to adverse effects like nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and headaches
- Long-term high intake can interfere with copper absorption and affect immune function
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking zinc supplements, especially in doses exceeding the RDA.
How much zinc should a 65 year old woman take?
For a 65-year-old woman:
- The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for zinc is 8mg
- This amount is generally sufficient for maintaining health in older adults
- Some studies suggest that older adults may benefit from slightly higher intakes (up to 15mg daily) due to decreased absorption
- Factors like diet, health conditions, and medication use may influence individual needs
It’s advisable for older adults to consult with their healthcare provider to determine the optimal zinc intake based on their specific health status and needs.
Zinc deficiency symptoms
Common symptoms of zinc deficiency include:
- Weakened immune system and frequent infections
- Slow wound healing
- Loss of taste or smell
- Hair loss
- Skin problems (e.g., acne, rashes)
- Decreased appetite
- Diarrhea
- Cognitive impairment and mood changes
- Growth retardation in children
- Reproductive issues and decreased libido
If experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Daily dose of zinc for adults
The recommended daily dose of zinc for adults varies:
- Adult men: 11mg per day
- Adult women: 8mg per day
- Pregnant women: 11mg per day
- Lactating women: 12mg per day
- Upper limit for all adults: 40mg per day
These recommendations are for dietary zinc intake. Supplemental zinc should be taken under medical supervision, as needs can vary based on individual health factors.
How much zinc should a 70 year old woman take?
For a 70-year-old woman:
- The RDA remains at 8mg per day, the same as for younger adult women
- However, some research suggests that older adults may benefit from slightly higher intakes (10-15mg daily) due to potential decreased absorption
- Factors such as diet quality, health conditions, and medication use can affect individual zinc needs
- Zinc status should be monitored, especially if on a restricted diet or taking medications that may interfere with zinc absorption




