Table of Contents
Are you feeling tired, rundown, or noticing changes in your taste or smell? These could be the First Sign of a Zinc Deficiency. Zinc is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, and even a mild deficiency can manifest in surprising ways. This article will delve into the subtle and not-so-subtle First Signs of a Zinc Deficiency, helping you understand the importance of this often-overlooked nutrient. Recognizing the First Sign of a Zinc Deficiency is crucial for early intervention and maintaining optimal health. Let’s explore the common indicators and learn how to ensure you’re getting enough zinc in your diet.
Brief The Article:
What is the first sign of a zinc deficiency?
- The first noticeable symptom is shortness of breath upon exertion
- This can manifest as difficulty breathing when exercising or climbing stairs
- Getting out of breath easily during physical activities is a key indicator
What happens when you’re low in zinc?
- Reduced levels of important antioxidants: glutathione, alpha tocopherol, and catalase
- Impaired detoxification of hydrogen peroxide
- Insufficient production of powerful antioxidants in the body
What you need to know about zinc and heart health
- Heart tissue produces high levels of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species)
- Heart cells have low antioxidant capacity, making them susceptible to damage
- Zinc deficiency can impair heart repair mechanisms
- This susceptibility to damage may contribute to heart disease being a leading cause of death
Clinical symptoms of zinc deficiency
- Lack of growth
- Anorexia
- Tissue necrosis
- Skin issues
- Digestive problems
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Hair loss
- Ulcers
So let’s dive into the details…
What is the first sign of a zinc deficiency?
Let’s answer the question what is the first sign of a zinc deficiency now clinically when you’re deficient in zinc all sorts of things happen a lack of growth anorexia tissue necrosis

you can actually get tissue dying from a lack of zinc all sorts of skin issues all sorts of digestive issues infection viruses bacteria hair loss ulcers and the list goes on and on you don’t have a major deficiency
but you’re just starting to become deficient in zinc well to answer that we need to kind of look at some other data number one
Clinical Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency:
- Lack of growth
- Anorexia
- Tissue necrosis
- Skin issues
- Digestive problems
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Hair loss
- Ulcers
What happens when you’re low in zinc?
When you’re low in zinc you will have a lowered amount of very specific antioxidants glutathione alpha tocopherol and catalase which has to do with the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide
so in other words, very powerful antioxidants in our bodies are dependent on zinc and without zinc you will not be able to produce these in sufficient amounts
Effects of Low Zinc Levels:
- Reduced levels of important antioxidants:
- Glutathione
- Alpha-tocopherol
- Catalase
- Impaired detoxification of hydrogen peroxide
- Insufficient production of powerful antioxidants
What you need to know about zinc
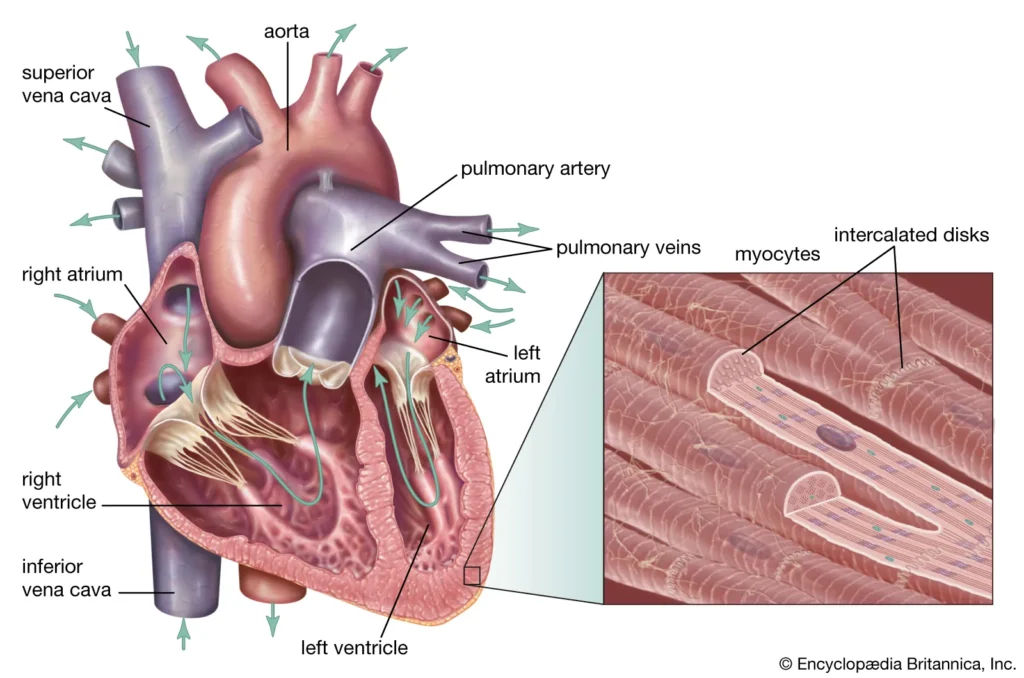
Now there’s some additional information i want to share with you cardiac tissue or heart tissue is the highest producer of something called ross
so just think about ross as something that creates a lot of oxidation and the heart cells as a tissue if we compare it to other tissues in the body has one the lowest antioxidant capacity now what does that mean
so in other words it becomes very susceptible to becoming damaged this is probably why the number one cause of death is heart disease the heart is not able to repair effectively and the first symptom is you’re going to get shortness of breath upon exertion
Important Facts About Zinc and Heart Health:
- Heart tissue produces high levels of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species)
- Heart cells have low antioxidant capacity
- This makes the heart susceptible to damage
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death
- Zinc deficiency can impair heart repair mechanisms
The first sign of a zinc deficiency

So let’s say you start to exercise or you run up the stairs and you’re out of breath easily that would be the first symptom of a zinc deficiency
so I remember as a kid living on sugar outside playing and noticing i was having a difficult time running up a hill i was like out of breath very easily i had no clue on what that was but it was probably a zinc deficiency due to all the sugar that was consuming
so if you have that symptom read a lot more of my Topics on zinc i put the links down below check it out
Identifying the First Sign of Zinc Deficiency:
- Shortness of breath upon exertion
- Difficulty breathing when exercising or climbing stairs
- Easily getting out of breath during physical activities
For more information
Summary
The first sign of a zinc deficiency is shortness of breath upon exertion.
What is the first sign of a zinc deficiency? Clinically, when you’re deficient in zinc, a lot of different things can happen, including:
• A lack of growth
• Anorexia
• Tissue necrosis
• Skin issues
• Digestive issues
• Infection
• Hair loss
• Ulcers
When you’re low in zinc, you’ll have a lowered amount of specific antioxidants, including:
• Glutathione
• Alpha-tocopherol
• Catalase
FAQ
What is a symptom of a zinc deficiency quizlet?
A common symptom of zinc deficiency often featured in quizlets is impaired wound healing. Other symptoms that might be included are:
- Decreased sense of taste and smell
- Hair loss
- Weakened immune function
- Skin problems like acne or rashes
- Delayed growth in children
Remember, quizlets may vary in their content, but these are frequently mentioned symptoms.
What is zinc deficiency characterised by?
Zinc deficiency is characterised by a wide range of symptoms due to zinc’s crucial role in many bodily functions. Key characteristics include:
- Growth retardation and delayed sexual maturation in children
- Impaired immune function leading to increased susceptibility to infections
- Cognitive impairment and mood changes
- Skin issues such as dermatitis and slow wound healing
- Hair loss or alopecia
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Impaired taste (hypogeusia) and smell
The severity and combination of these symptoms can vary depending on the degree of deficiency.
Is being zinc deficient a sign of being tired?
Yes, fatigue or tiredness can be a sign of zinc deficiency. Zinc plays a crucial role in many metabolic processes, including energy production. When zinc levels are low, it can lead to:
- Decreased energy levels and increased fatigue
- Weakened immune system, which can make you more susceptible to illnesses that cause tiredness
- Poor sleep quality, as zinc is involved in the production of melatonin
- Mood changes, including depression, which can manifest as tiredness
However, it’s important to note that fatigue can be caused by many factors, and zinc deficiency should be confirmed through proper medical testing.
Signs of zinc deficiency in females
While zinc deficiency can affect both genders, some signs may be more noticeable or specific to females:
- Irregular menstrual cycles or menstrual problems
- Fertility issues or difficulty conceiving
- Hair loss or thinning hair
- Brittle or weak nails
- Skin problems, including acne or slow wound healing
- Weakened immune system leading to frequent infections
- Taste alterations or loss of appetite
- Mood changes, including depression or irritability
It’s important for women to maintain adequate zinc levels, especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding when zinc requirements increase.
Zinc deficiency neurological symptoms
Zinc plays a crucial role in brain function and neurological health. Neurological symptoms of zinc deficiency can include:
- Cognitive impairment and difficulty with memory or concentration
- Mood disorders, including depression and irritability
- Changes in behavior or emotional responses
- Impaired motor function or coordination
- Altered sensory perception, particularly taste and smell
- Increased risk of neurological conditions like epilepsy or Alzheimer’s disease
- Headaches or migraines
- In severe cases, potential developmental delays in children
These symptoms can vary in severity and may be accompanied by other signs of zinc deficiency.
Zinc deficiency signs
Zinc deficiency can manifest in various ways throughout the body. Common signs include:
- Delayed wound healing
- Frequent infections due to weakened immune function
- Hair loss or thinning
- Skin problems like acne, rashes, or dermatitis
- Loss of appetite or altered taste perception
- Diarrhea
- Growth retardation in children
- Decreased sense of smell
- Fertility issues in both men and women
- Night blindness or difficulty seeing in low light
If you suspect zinc deficiency, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Zinc deficiency symptoms skin
The skin can be significantly affected by zinc deficiency. Common skin-related symptoms include:
- Slow wound healing
- Acne or worsening of existing acne
- Eczema or dermatitis
- Dry, rough skin
- Rashes or skin lesions
- Cracked or peeling skin, especially on hands or feet
- Increased susceptibility to sunburn
- Pale or dull-looking skin
- Angular cheilitis (cracks at the corners of the mouth)
Zinc deficiency diseases
Zinc deficiency can contribute to or exacerbate various diseases and health conditions:
- Acrodermatitis enteropathica (a rare inherited disorder of zinc absorption)
- Growth retardation and delayed puberty in children
- Impaired immune function leading to increased susceptibility to infections
- Pneumonia, especially in children
- Diarrheal diseases
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Male hypogonadism
- Osteoporosis
- Diabetes (zinc plays a role in insulin production and glucose metabolism)
- Certain neurological disorders
Treatment of zinc deficiency
Treatment for zinc deficiency typically involves:
- Zinc supplementation: Oral zinc supplements in various forms (e.g., zinc sulfate, zinc gluconate)
- Dietary changes: Increasing intake of zinc-rich foods (e.g., oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, lentils)
- Addressing underlying causes: Treating conditions that may be causing zinc malabsorption
- Adjusting medications: Some medications can interfere with zinc absorption
- Regular monitoring: Blood tests to check zinc levels and ensure proper dosage
- In severe cases: Intravenous zinc supplementation may be necessary
Symptoms of zinc deficiency in males
- Low testosterone levels and reduced libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Prostate problems
- Male pattern baldness or hair loss
- Delayed sexual maturation in adolescents
- Reduced sperm count or quality, leading to fertility issues
- Increased risk of male breast development (gynecomastia)
- Muscle wasting or reduced muscle mass
- Impaired wound healing, especially after surgery
Men with these symptoms should consider getting their zinc levels checked, especially if they have risk factors for deficiency.
Zinc deficiency face
- Acne or worsening of existing acne
- Pale or sallow complexion
- Dry, flaky skin
- Rashes or dermatitis
- Angular cheilitis (cracks at the corners of the mouth)
- Hair loss, including eyebrows and eyelashes
- Dark circles under the eyes
- Delayed wound healing of facial cuts or abrasions
- Seborrheic dermatitis (red, scaly patches)