Table of Contents
Did you know that the trace mineral zinc plays a crucial role in the intricate dance of hormones within your body? From testosterone and estrogen to growth hormone and insulin, zinc is a key player in maintaining hormonal balance and overall health. Let’s delve into the fascinating relationship between zinc and hormones and discover how this essential nutrient can impact your well-being.
Brief The Article:
Zinc and Male Hormones:
- Zinc is essential for the production of testosterone in men.
- Zinc deficiency can lead to hypogonadism (shrinking of the testicles).
- Zinc inhibits the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone to DHT (dihydrotestosterone), helping to prevent excessive DHT levels that can contribute to hair loss and prostate enlargement.
Zinc and Female Hormones:
- Zinc supports the production of both estrogen and progesterone in women.
- Zinc can help increase progesterone levels in menopausal women, who often experience a progesterone deficiency.
- Zinc can also help regulate estrogen levels in menopausal women.
- Zinc acts as an aromatase inhibitor, preventing the excessive conversion of testosterone to estrogen, which can lead to estrogen dominance in both men and women.
Zinc and Other Key Hormones:
- Zinc supports healthy levels of growth hormone, which is crucial for fat-burning, anti-aging, and protein synthesis.
- Zinc is essential for the conversion of T4 (inactive thyroid hormone) to T3 (active thyroid hormone).
- Zinc is also required for the production of thyroid hormone by the pituitary and thyroid glands.
- Zinc improves insulin sensitivity and reduces insulin resistance, helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Overall Importance of Zinc:
- Zinc is a vital trace mineral that plays a crucial role in numerous biochemical reactions and hormonal processes.
- Maintaining adequate zinc levels is essential for overall health and hormonal balance.
Key Takeaway:
Zinc is a crucial nutrient for maintaining hormonal balance in both men and women. Ensuring adequate zinc intake through diet or supplementation can significantly impact various aspects of health, including reproductive health, metabolism, and overall well-being.
So let’s dive into the details…
Zinc and Hormones

You know zinc is a fascinating trace mineral. It’s involved in so many different biochemical reactions but today we’re going to talk about the relationship between zinc and hormones.
Now zinc is involved in so many different biochemical pathways but it’s majorly involved in quite a few of your hormones. In fact, it’s involved in all of your major hormones. Let’s go through this.
How Zinc Controls Many Key Hormones
Zinc and Hormones (Pituitary )
First of all, there are two pituitary hormones called follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone and they send signals down to the gonads both the ovaries and the testicle.
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Zinc and hormones (Testosterone)
So in men luteinizing hormone LH increases testosterone so zinc increases testosterone. If you’re zinc deficient your gonads actually shrink you get what’s called hypogonadism. So zinc will increase your testosterone.
Key points:
- Zinc increases testosterone
- Zinc deficiency can lead to hypogonadism
Zinc and DHT (Dihydrotestosterone)

Now there’s also another situation where you have testosterone turning into a very powerful form of testosterone called DHT through a very specific enzyme called 5-alpha reductase.
So if there’s too much of this enzyme you get too much DHT and one of the problems you get is you get hair loss another problem is prostate enlargement.
So zinc helps act as an inhibitor of five alpha reductase limiting the amount of DHT you get.
Zinc and Hormones ( Female )
When a female follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone control estrogen and progesterone zinc will help increase progesterone as well as estrogen unless you have estrogen dominance which i’m going to get to in a second.
But so many women during menopause end up having a major deficiency in progesterone and if they took a little zinc they would actually have more progesterone they would have better ratios of progesterone to estrogen.
Zinc’s effects on female hormones:
- Increases progesterone
- Helps balance estrogen levels
- Beneficial during menopause
Zinc and hormones (Estrogen )

Now if a woman is menopausal she typically has a lot less estrogen and so zinc can help bring that up to a correct level
you also have another enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogen it’s called aromatase and if there’s too much of this hormone you’re going to get estrogen dominance.
Now this can happen in men and women and one of the things that will increase this enzyme is plastics in the environment and it just so happens that a really good aromatase inhibitor is zinc
so zinc will help you from developing too much estrogen if you’re a male or a female.
- Zinc can help restore estrogen levels in menopausal women.
- Aromatase is an enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen.
- Excessive aromatase activity can lead to estrogen dominance.
- Estrogen dominance can occur in both men and women, often exacerbated by environmental factors like plastics.
- Zinc acts as an aromatase inhibitor, helping to prevent estrogen dominance.
Zinc and Hormones( Growth )
Then we get to growth hormone which is the main fat-burning hormone it’s an anti-aging hormone it has everything to do with regulating and helping you make new proteins in the body
and it just so happens in zinc supports normal growth hormone levels as well as another hormone that is an extension of growth hormone which is made by your liver called IGF number one.
- Growth hormone is crucial for fat-burning, anti-aging, and protein synthesis.
- Zinc supports healthy growth hormone levels and the production of IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1), another important hormone.
Zinc and hormones (Thyroid Function)
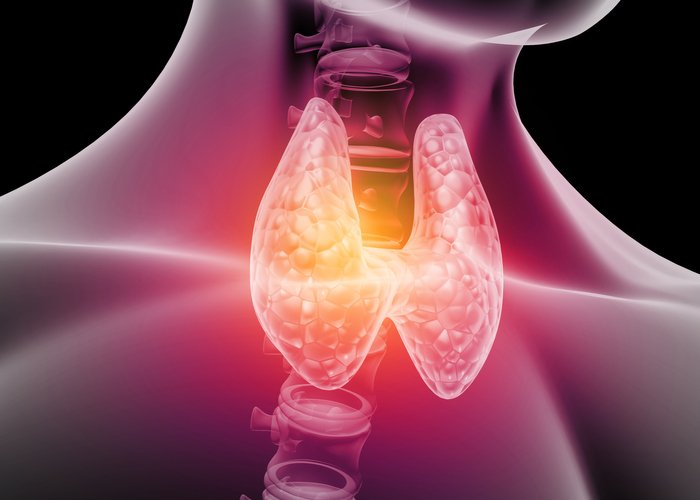
Then we get to the thyroid in order for you to convert T4 the inactive form of the thyroid hormone to T3 which is the active form you need zinc you also need selenium and you also need iodine but zinc is very important in this conversion.
Also zinc is needed by the pituitary and the thyroid to make more of its thyroid hormone.
- Zinc is essential for converting T4 (inactive thyroid hormone) to T3 (active thyroid hormone).
- Selenium and iodine are also necessary for this conversion.
- Zinc is required by the pituitary and thyroid glands for thyroid hormone production.
Zinc and hormones (Insulin)

And then lastly let’s talk about insulin. Okay insulin is a very important hormone and it’s very important not to have too much of this hormone so zinc helps increase insulin sensitivity as well as helps inhibit insulin resistance thereby decreasing the amount of insulin.
Zinc’s effects on insulin:
- Increases insulin sensitivity
- Inhibits insulin resistance
- Helps regulate blood sugar levels
Zinc is intimately involved with so many key hormones. So zinc is all about helping your blood sugars helping regulate insulin levels zinc is intimately involved with so many key hormones.
Summary
Zinc is involved in many biochemical pathways, and it’s involved in all of your major hormones.
How zinc affects your hormones:
• Zinc increases testosterone
• Zinc helps inhibit 5-alpha reductase (limiting DHT)
• Zinc helps increase progesterone and estrogen (unless you have estrogen dominance)
• Zinc helps inhibit aromatase (it will help keep you from developing too much estrogen)
• Zinc supports normal growth hormone levels and IGF-1
• Zinc supports the conversion of T4 to T3
• Zinc is needed to make more thyroid hormone
• Zinc helps increase insulin sensitivity, and it helps inhibit insulin resistance
Additional-resources
FAQ
Can zinc cure hormonal imbalance?
While zinc cannot “cure” hormonal imbalance, it plays a crucial role in hormone regulation. Zinc is essential for the proper functioning of many hormones, including insulin, thyroid hormones, and sex hormones. Adequate zinc intake can help support hormonal balance, but it’s not a standalone cure. A balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and consultation with a healthcare professional are all important factors in addressing hormonal imbalances.
Is zinc associated with the hormone insulin?
Yes, zinc is closely associated with insulin. Zinc plays a vital role in the synthesis, storage, and secretion of insulin. It’s also involved in maintaining the structural integrity of insulin. Adequate zinc levels are crucial for proper insulin function and glucose metabolism. In fact, the pancreatic beta cells, which produce insulin, have one of the highest concentrations of zinc in the body. Zinc deficiency can impair insulin secretion and contribute to insulin resistance, potentially increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
What hormone is associated with zinc?
Zinc is associated with multiple hormones in the body. Some of the key hormones associated with zinc include:
- Insulin: Zinc is crucial for insulin synthesis, storage, and secretion.
- Thyroid hormones: Zinc is necessary for the production and function of thyroid hormones.
- Sex hormones: Zinc plays a role in the production and regulation of testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone.
- Growth hormone: Zinc is involved in the secretion and function of growth hormone.
- Cortisol: Zinc influences the production and regulation of this stress hormone.
These associations highlight the importance of zinc in maintaining overall hormonal balance in the body.
How does zinc affect the endocrine system?
Zinc affects the endocrine system in multiple ways:
- Hormone Production: Zinc is involved in the synthesis of various hormones, including insulin, thyroid hormones, and sex hormones.
- Hormone Receptor Function: Zinc is necessary for the proper functioning of hormone receptors, which are crucial for hormones to exert their effects on target cells.
- Enzyme Activity: Many enzymes involved in hormone metabolism require zinc as a cofactor.
- Glandular Function: Zinc supports the health and function of endocrine glands, such as the thyroid, pancreas, and reproductive organs.
- Hormone Transport: Zinc influences the production of hormone-binding proteins, which are important for hormone transport in the bloodstream.
- Hormone Signaling: Zinc is involved in intracellular signaling pathways that mediate hormone actions.
By influencing these various aspects, zinc plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and proper functioning of the endocrine system.
Does zinc help hormones?
Yes, zinc does help hormones in several ways:
- Supports hormone production and secretion
- Enhances hormone receptor function
- Aids in hormone metabolism
- Maintains endocrine gland health
- Influences hormone signaling pathways
Adequate zinc levels are essential for maintaining hormonal balance and overall endocrine health. However, it’s important to note that while zinc is crucial, it works in conjunction with other nutrients and lifestyle factors to support optimal hormone function.
Does zinc affect growth hormone?
Yes, zinc does affect growth hormone (GH) in several ways:
- GH Secretion: Zinc stimulates the release of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), which in turn promotes GH secretion from the pituitary gland.
- GH Receptor Function: Zinc is necessary for the proper functioning of GH receptors, ensuring that target tissues can respond effectively to GH.
- IGF-1 Production: Zinc is involved in the production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which mediates many of the growth-promoting effects of GH.
- Cell Division and Growth: Zinc is essential for DNA synthesis and cell division, processes that are crucial for the growth-promoting effects of GH.
While zinc is important for GH function, it’s part of a complex system involving multiple nutrients and factors that influence growth and development.
Does zinc increase androgens?
Zinc can influence androgen levels, particularly testosterone:
- Testosterone Production: Zinc is necessary for the enzymes involved in testosterone synthesis.
- Enzyme Inhibition: Zinc can inhibit the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone to estrogen, potentially leading to higher testosterone levels.
- Luteinizing Hormone: Zinc supports the production of luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates testosterone production in the testes.
- Free Testosterone: Zinc may increase levels of free (bioavailable) testosterone by inhibiting the enzyme that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
While zinc is important for androgen production, its effects can vary depending on an individual’s baseline zinc status, overall health, and other factors. Excessive zinc supplementation is not recommended and may not necessarily lead to increased androgen levels.
Does zinc produce progesterone?
Zinc doesn’t directly produce progesterone, but it plays a supportive role in progesterone production and function:
- Enzyme Support: Zinc is a cofactor for enzymes involved in steroid hormone synthesis, including progesterone.
- Ovarian Function: Zinc supports overall ovarian health, which is crucial for progesterone production.
- Luteinizing Hormone: Zinc influences the production of luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates progesterone secretion from the corpus luteum.
- Receptor Function: Zinc may play a role in the proper functioning of progesterone receptors.
While zinc is important for hormonal balance, including progesterone, it’s part of a complex system involving multiple nutrients and factors. Adequate zinc intake supports overall reproductive health and hormone production, but it doesn’t directly produce progesterone.
Zinc and estrogen dominance
Zinc may play a role in managing estrogen dominance:
- Aromatase Inhibition: Zinc can inhibit the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone to estrogen, potentially helping to balance estrogen levels.
- Estrogen Receptor Modulation: Zinc may influence estrogen receptor function, potentially affecting how the body responds to estrogen.
- Liver Support: Zinc supports liver function, which is crucial for estrogen metabolism and elimination.
- Antioxidant Properties: As an antioxidant, zinc may help protect against oxidative stress associated with hormonal imbalances.
While zinc may be beneficial in cases of estrogen dominance, it’s important to address the underlying causes and consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive approach to hormonal balance.
Does zinc increase testosterone in females
Zinc can influence testosterone levels in females, but the effects are generally more subtle than in males:
- Ovarian Function: Zinc supports overall ovarian health, which is responsible for producing small amounts of testosterone in females.
- Enzyme Support: Zinc is a cofactor for enzymes involved in steroid hormone synthesis, including testosterone.
- PCOS Consideration: In women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), who often have elevated testosterone levels, zinc supplementation may help regulate hormone balance.
- Individual Variation: The effects of zinc on testosterone in females can vary based on individual factors such as age, overall health, and existing zinc status.
It’s important to note that while zinc is essential for hormonal health, excessive supplementation is not recommended and may not necessarily lead to significant increases in testosterone in females. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen.
How long does it take for zinc to increase testosterone
The time it takes for zinc to potentially increase testosterone can vary:
- Existing Deficiency: In cases of zinc deficiency, improvements in testosterone levels may be seen within a few weeks to a few months of supplementation.
- Individual Factors: The timeline can vary based on age, overall health, diet, and lifestyle factors.
- Dosage: The amount of zinc supplementation can influence the rate of change.
- Consistency: Regular, consistent zinc intake is key for potential long-term effects on testosterone levels.
- Research Findings: Some studies have shown changes in testosterone levels after 4-6 weeks of zinc supplementation, while others suggest longer periods may be necessary.
It’s important to note that zinc supplementation alone may not significantly increase testosterone in individuals who are not deficient. A balanced approach to nutrition and lifestyle is crucial for optimal hormonal health.
Does zinc lower estrogen in males
Zinc may indirectly influence estrogen levels in males:
- Aromatase Inhibition: Zinc can inhibit the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone to estrogen, potentially leading to lower estrogen levels.
- Testosterone Support: By supporting healthy testosterone levels, zinc may help maintain a balanced testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
- Liver Function: Zinc supports liver health, which is crucial for proper estrogen metabolism and elimination.
- Antioxidant Effects: As an antioxidant, zinc may help reduce oxidative stress, which can influence hormonal balance.
While zinc may play a role in estrogen regulation, its effects can vary among individuals. It’s important to maintain a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on hormonal health.
How much zinc to lower testosterone in females
It’s important to note that zinc supplementation is not typically used to lower testosterone in females. In fact, zinc is essential for overall hormonal balance:
- Balanced Approach: The goal should be to achieve hormonal balance rather than specifically lowering testosterone.
- Individual Variations: The effect of zinc on testosterone can vary greatly among individuals.
- Professional Guidance: Any attempt to alter hormone levels should be done under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
- Recommended Daily Allowance: For adult women, the RDA for zinc is 8-11 mg per day, which is generally sufficient for maintaining overall health.
- Caution: Excessive zinc intake can lead to adverse effects and may disrupt the balance of other minerals in the body.
If you’re concerned about high testosterone levels, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options tailored to your individual needs.
Zinc for hirsutism reviews
Zinc has been studied for its potential effects on hirsutism, which is excessive hair growth in women:
- Hormonal Balance: Zinc may help regulate hormones that contribute to hirsutism, particularly in cases of PCOS.
- 5-alpha Reductase Inhibition: Some studies suggest zinc may inhibit 5-alpha reductase, an enzyme that converts testosterone to the more potent dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
- Mixed Results: Reviews of zinc for hirsutism show mixed results, with some individuals reporting improvements while others see little effect.
- Complementary Approach: Zinc is often used as part of a broader treatment plan for hirsutism, including dietary changes and other supplements.
- Individual Variation: The effectiveness of zinc for hirsutism can vary based on the underlying cause and individual factors.
While some individuals report positive effects, more research is needed to fully understand the role of zinc in managing hirsutism. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive approach to treatment.
Zinc for hormonal imbalance
Zinc plays a crucial role in maintaining hormonal balance:
- Thyroid Function: Zinc is essential for the production and function of thyroid hormones.
- Insulin Regulation: Zinc is involved in insulin synthesis, storage, and secretion.
- Sex Hormones: Zinc supports the production and regulation of testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone.
- Stress Response: Zinc influences the production and regulation of cortisol, the stress hormone.
- Enzyme Support: Many enzymes involved in hormone metabolism require zinc as a cofactor.
While zinc supplementation may be beneficial for some hormonal imbalances, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. A balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and consultation with a healthcare professional are all important factors in addressing hormonal imbalances.
Does zinc increase estrogen levels in males
Zinc generally does not increase estrogen levels in males. In fact, it may have the opposite effect:
- Aromatase Inhibition: Zinc can inhibit the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone to estrogen, potentially leading to lower estrogen levels.
- Testosterone Support: By supporting healthy testosterone levels, zinc may help maintain a balanced testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
- Hormonal Balance: Zinc plays a crucial role in overall hormonal balance, including the regulation of sex hormones.
- Individual Variation: The effects of zinc on hormone levels can vary based on factors such as age, overall health, and existing zinc status.